WMS:Mapping to Feature Objects: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
While future versions of WMS may be able to process some commands directly from the GIS data layers, currently you must map all features you wish to use as part of model development to feature objects in a map coverage. One way to do this is to import an entire shapefile directly to map coverage (this is the only way available in previous versions), but often the extents of the GIS data layer are much larger (i.e. an entire state) and so it may be more efficient to select only those GIS features (points, lines, polygons) that overlay your study area and map those to feature objects in a map coverage. | While future versions of WMS may be able to process some commands directly from the GIS data layers, currently you must map all features you wish to use as part of model development to feature objects in a map coverage. One way to do this is to import an entire shapefile directly to map coverage (this is the only way available in previous versions), but often the extents of the GIS data layer are much larger (i.e. an entire state) and so it may be more efficient to select only those GIS features (points, lines, polygons) that overlay your study area and map those to feature objects in a map coverage. | ||
A mapping wizard guides you through the process of converting your GIS data layer features to feature objects in a map coverage. Before beginning the mapping process you should first go to the map module and make sure that the currently active coverage is the coverage you wish to map GIS data layer features to. For example, the default coverage in WMS is a drainage coverage and so if you are about to map soil polygons you will want to create a new coverage and make sure that it has an attribute set of Soil Type. After making sure you will be mapping to the correct coverage select the polygons which overlay your study area and you wish to map (this is done with the selection tool(s) in the GIS module). If you wish to map all features, you can choose the '''Select All''' command from the | A mapping wizard guides you through the process of converting your GIS data layer features to feature objects in a map coverage. Before beginning the mapping process you should first go to the map module and make sure that the currently active coverage is the coverage you wish to map GIS data layer features to. For example, the default coverage in WMS is a drainage coverage and so if you are about to map soil polygons you will want to create a new coverage and make sure that it has an attribute set of Soil Type. After making sure you will be mapping to the correct coverage select the polygons which overlay your study area and you wish to map (this is done with the selection tool(s) in the GIS module). If you wish to map all features, you can choose the '''Select All''' command from the ''Edit Window'', or just move to the '''Mapping''' command (you will be prompted if you want to convert all features since none are selected). | ||
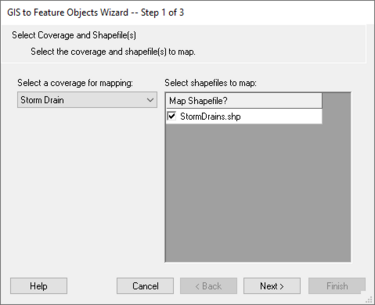
If you have ArcObjects enabled, you will see that the '''ArcObjects→Feature Objects''' command is activated, whereas if you do not have ArcObjects enabled, you will see that the '''Shapes→Feature Objects''' command is activated. After choosing the appropriate mapping command you will see the mapping wizard shown below. This wizard will guide you through the rest of the process. The first dialog in the mapping wizard contains instructions and marks the beginning point of mapping for selected features. The first of two steps is to map the attribute fields of the features to attributes used by WMS. WMS recognizes some attribute names as commonly used for certain attributes and maps them automatically (i.e. HYDRGRP for hydrologic soil groups and LU_CODE for land use ID's). | If you have ArcObjects enabled, you will see that the '''ArcObjects→Feature Objects''' command is activated, whereas if you do not have ArcObjects enabled, you will see that the '''Shapes→Feature Objects''' command is activated. After choosing the appropriate mapping command you will see the mapping wizard shown below. This wizard will guide you through the rest of the process. The first dialog in the mapping wizard contains instructions and marks the beginning point of mapping for selected features. The first of two steps is to map the attribute fields of the features to attributes used by WMS. WMS recognizes some attribute names as commonly used for certain attributes and maps them automatically (i.e. HYDRGRP for hydrologic soil groups and LU_CODE for land use ID's). | ||
Revision as of 15:41, 29 May 2013
While future versions of WMS may be able to process some commands directly from the GIS data layers, currently you must map all features you wish to use as part of model development to feature objects in a map coverage. One way to do this is to import an entire shapefile directly to map coverage (this is the only way available in previous versions), but often the extents of the GIS data layer are much larger (i.e. an entire state) and so it may be more efficient to select only those GIS features (points, lines, polygons) that overlay your study area and map those to feature objects in a map coverage.
A mapping wizard guides you through the process of converting your GIS data layer features to feature objects in a map coverage. Before beginning the mapping process you should first go to the map module and make sure that the currently active coverage is the coverage you wish to map GIS data layer features to. For example, the default coverage in WMS is a drainage coverage and so if you are about to map soil polygons you will want to create a new coverage and make sure that it has an attribute set of Soil Type. After making sure you will be mapping to the correct coverage select the polygons which overlay your study area and you wish to map (this is done with the selection tool(s) in the GIS module). If you wish to map all features, you can choose the Select All command from the Edit Window, or just move to the Mapping command (you will be prompted if you want to convert all features since none are selected).
If you have ArcObjects enabled, you will see that the ArcObjects→Feature Objects command is activated, whereas if you do not have ArcObjects enabled, you will see that the Shapes→Feature Objects command is activated. After choosing the appropriate mapping command you will see the mapping wizard shown below. This wizard will guide you through the rest of the process. The first dialog in the mapping wizard contains instructions and marks the beginning point of mapping for selected features. The first of two steps is to map the attribute fields of the features to attributes used by WMS. WMS recognizes some attribute names as commonly used for certain attributes and maps them automatically (i.e. HYDRGRP for hydrologic soil groups and LU_CODE for land use ID's).
The second step marks the end of the wizard, and after selecting Finish, all selected features will be converted to feature objects within the active coverage. Attributes of mapped fields will be saved accordingly as attributes of the feature objects.
Related Topics
| [hide] WMS – Watershed Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | Terrain Data • Drainage • Map • Hydrologic Modeling • River • GIS • 2D Grid • 2D Scatter |  |
| Models: | CE-QUAL-W2 • GSSHA • HEC-1 • HEC-HMS • HEC-RAS • HSPF • MODRAT • NSS • OC Hydrograph • OC Rational • Rational • River Tools • Storm Drain • SMPDBK • SWMM • TR-20 • TR-55 | |
| Toolbars: | Modules • Macros • Units • Digitize • Static Tools • Dynamic Tools • Drawing • Get Data Tools | |
| Aquaveo | ||