WMS:Feature Objects to ArcHydro Geodatabase: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
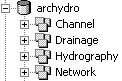
The '''Feature Objects → ArcHydro Geodatabase''' command is similar to the [[WMS:Feature Objects to Geodatabase|'''Feature Objects → Geodatabase''']] command, except that the geodatabase is written out in a particular format. The ArcHydro geodatabase model was developed to create a common GIS framework for storing water resources data. ArcHydro accounts for stream networks and their associated topology, along with the drainage, channel, and hydrography data defining the project. For more information, see Maidment (2002). These data are stored in four different feature datasets within the geodatabase. | The '''Feature Objects → ArcHydro Geodatabase''' command is similar to the [[WMS:Feature Objects to Geodatabase|'''Feature Objects → Geodatabase''']] command, except that the geodatabase is written out in a particular format. The ArcHydro geodatabase model was developed to create a common GIS framework for storing water resources data. ArcHydro accounts for stream networks and their associated topology, along with the drainage, channel, and hydrography data defining the project. For more information, see Maidment (2002). These data are stored in four different feature datasets within the geodatabase. | ||
:[[Image:WMSArcHydro001.png]] | :[[Image:WMSArcHydro001.png]] | ||
In order to create an ArcHydro geodatabase from WMS, first switch to the GIS module and enable ArcObjects. WMS uses the feature objects stored in each coverage to build the geodatabase. | |||
In order to create an ArcHydro geodatabase from WMS, | |||
Set up and build feature objects to add to the geodatabase, and define a coordinate system for the project. Vector data are stored in feature datasets and feature classes in the geodatabase, which require a common spatial reference. The spatial reference in the geodatabase is defined from the current coordinate system in WMS. | Set up and build feature objects to add to the geodatabase, and define a coordinate system for the project. Vector data are stored in feature datasets and feature classes in the geodatabase, which require a common spatial reference. The spatial reference in the geodatabase is defined from the current coordinate system in WMS. | ||
| Line 11: | Line 9: | ||
A WMS drainage coverage is used to build the Network, Drainage, and part of the Hydrography feature datasets. 1D Hydraulic Centerline and 1D Hydraulic Cross Section coverages are used to define the Channel feature dataset. If there is a DEM, it canl be used to create a raster grid. Each TIN in memory can also be used to create a feature dataset suitable for building a TIN within a GIS. | A WMS drainage coverage is used to build the Network, Drainage, and part of the Hydrography feature datasets. 1D Hydraulic Centerline and 1D Hydraulic Cross Section coverages are used to define the Channel feature dataset. If there is a DEM, it canl be used to create a raster grid. Each TIN in memory can also be used to create a feature dataset suitable for building a TIN within a GIS. | ||
Once the data and spatial reference are defined, select '''Feature Objects → ArcHydro Geodatabase''' from the ''Mapping'' menu in the GIS module. At this point, | Once the data and spatial reference are defined, select '''Feature Objects → ArcHydro Geodatabase''' from the ''Mapping'' menu in the GIS module. At this point, a prompt will ask if wanting to create a raster grid from the DEM in WMS, if if there is one loaded. Then a prompt will ask whether to create a feature dataset consisting of a TIN boundary, TIN breaklines, and TIN vertices if there is a TIN in memory. WMS will build the ArcHydro geodatabase based on the coverages and data created. WMS will then create the raster grid and TIN dataset if there is this data in the WMS project and elected to build them. | ||
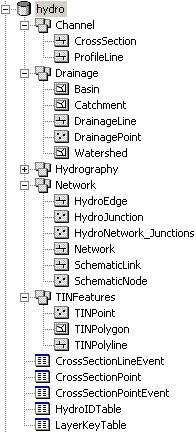
Once WMS has finished building the geodatabase, view the results in ArcCatalog® or ArcMap®. WMS will have created a new geodatabase with for feature datasets according to the ArcHydro data model, along with an additional feature dataset for the TIN (if applicable). WMS will also create the necessary tables for the model. | |||
:[[Image:WMSArcHydro002.png]] | :[[Image:WMSArcHydro002.png]] | ||
| Line 27: | Line 24: | ||
{{WMSMain}} | {{WMSMain}} | ||
[[Category:WMS GIS|F]] | [[Category:WMS GIS|F]] | ||
[[Category:WMS Feature Objects| | [[Category:WMS Feature Objects|ArcHydro]] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:33, 31 January 2017
The Feature Objects → ArcHydro Geodatabase command is similar to the Feature Objects → Geodatabase command, except that the geodatabase is written out in a particular format. The ArcHydro geodatabase model was developed to create a common GIS framework for storing water resources data. ArcHydro accounts for stream networks and their associated topology, along with the drainage, channel, and hydrography data defining the project. For more information, see Maidment (2002). These data are stored in four different feature datasets within the geodatabase.
In order to create an ArcHydro geodatabase from WMS, first switch to the GIS module and enable ArcObjects. WMS uses the feature objects stored in each coverage to build the geodatabase.
Set up and build feature objects to add to the geodatabase, and define a coordinate system for the project. Vector data are stored in feature datasets and feature classes in the geodatabase, which require a common spatial reference. The spatial reference in the geodatabase is defined from the current coordinate system in WMS.
A WMS drainage coverage is used to build the Network, Drainage, and part of the Hydrography feature datasets. 1D Hydraulic Centerline and 1D Hydraulic Cross Section coverages are used to define the Channel feature dataset. If there is a DEM, it canl be used to create a raster grid. Each TIN in memory can also be used to create a feature dataset suitable for building a TIN within a GIS.
Once the data and spatial reference are defined, select Feature Objects → ArcHydro Geodatabase from the Mapping menu in the GIS module. At this point, a prompt will ask if wanting to create a raster grid from the DEM in WMS, if if there is one loaded. Then a prompt will ask whether to create a feature dataset consisting of a TIN boundary, TIN breaklines, and TIN vertices if there is a TIN in memory. WMS will build the ArcHydro geodatabase based on the coverages and data created. WMS will then create the raster grid and TIN dataset if there is this data in the WMS project and elected to build them.
Once WMS has finished building the geodatabase, view the results in ArcCatalog® or ArcMap®. WMS will have created a new geodatabase with for feature datasets according to the ArcHydro data model, along with an additional feature dataset for the TIN (if applicable). WMS will also create the necessary tables for the model.
Related Topics
WMS – Watershed Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | Terrain Data • Drainage • Map • Hydrologic Modeling • River • GIS • 2D Grid • 2D Scatter |  |
| Models: | CE-QUAL-W2 • GSSHA • HEC-1 • HEC-HMS • HEC-RAS • HSPF • MODRAT • NSS • OC Hydrograph • OC Rational • Rational • River Tools • Storm Drain • SMPDBK • SWMM • TR-20 • TR-55 | |
| Toolbars: | Modules • Macros • Units • Digitize • Static Tools • Dynamic Tools • Drawing • Get Data Tools | |
| Aquaveo | ||