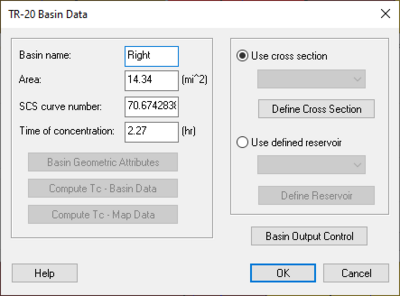
WMS:TR-20 Basin Data
General information for each basin is entered by selecting a basin and choosing the Basin Data dialog. If multiple basins are selected, some fields will not be able to be edited (e.g. Basin name and Area), while others will be "grayed out". These other fields are in Multi-select mode. If selecting and assigning data to these fields, this data is assigned to all the selected sub-basins.
Basin Name: – Each hydrograph station should be identified with a unique name. This name is specific to TR-20 files created by WMS and is used to identify the basin in the file so that resulting hydrographs from a model run can be read back into WMS and associated with the basin. The name can not be more than six characters long. By default WMS uses the basin ID number followed by a "B" for the name, but a descriptive name is generally more useful.
Area: – When a TIN, DEM, or map-based model is present, basin areas and slopes can be computed automatically using the Compute Basin Data command in the TIN or DEM Drainage module menus, or in the Feature Objects Map module menu. If a TIN, DEM, or map data are not present, areas and slopes must be entered interactively using the topological tree as a map. Areas should be entered in square miles.
SCS Curve Number: – Curve Number refers to the SCS curve number for rainfall/ losses on snow-free ground.
NOTE: Composite curve numbers can be computed automatically using a land use and hydrologic soil group coverages.
Time of Concentration – Time of concentration should be in hours for the unit hydrograph. Several different equations exist for determining the time of concentration. Two different methods exist for computing the time of concentration using computed basin data or using map data. The list of basin geometric attributes computed automatically when basins have been delineated from a TIN can be useful in many of these equations. These attributes can be viewed and edited from within the TR-20 Basin Data dialog by choosing the Basin Geometrical Attributes button.
Basin Geometric Attributes – Select this to open up the Basin Geometric Attributes. When drainage data are computed, select this button to view and edit the geometric attributes of a basin, including the basin area, the flow length, and the basin slope. The different basin attributes can be viewed and edited only after computing the basin data. The basin data may be computed by selecting the Compute Basin Data command in the TIN or DEM Drainage module menus, or in the Feature Objects Map module menu.
Compute tc-Basin Data – Pressing this button will bring up the Unit hydrograph parameter computation dialog. In this dialog, define the type of computation method to use in computing the time of concentration for TR-20. After exiting this dialog, the time of concentration, lag time, time to peak, and Snyder coefficient will be calculated. Many of these coefficients and times can be used in HEC-1 models, and the time of concentration can be used in TR-20 watershed models. By de-selecting the Do not auto-recompute parameters option, unit hydrograph parameters will be automatically re-calculated when the basin area is re-computed or other basin parameters are changed.
- See Travel Times from Basin Data for more information.
Compute tc-Map Data – Times of concentration may also be computed using a time computation coverage. The basin time of concentration dialog is accessed by selecting the Compute TC – Map Data button.
Use Cross Section – Select this option to use a defined Cross Section for the basin runoff computations.
Define Cross Section – To define a Cross Section, the elevation, discharge, and end area must be defined for different intervals. Select to bring up the XY Series Editor dialog.
Use Defined Reservoir – Select this option to use a defined reservoir for the basin runoff computations.
Define Reservoir – By selecting the Define Reservoir button, define a reservoir to use in the runoff computations. To define a reservoir, the elevation, discharge, and storage must be defined for different intervals.
Basin Output Control – Select to control the output of the basin.
Related Topics
| [hide] WMS – Watershed Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | Terrain Data • Drainage • Map • Hydrologic Modeling • River • GIS • 2D Grid • 2D Scatter |  |
| Models: | CE-QUAL-W2 • GSSHA • HEC-1 • HEC-HMS • HEC-RAS • HSPF • MODRAT • NSS • OC Hydrograph • OC Rational • Rational • River Tools • Storm Drain • SMPDBK • SWMM • TR-20 • TR-55 | |
| Toolbars: | Modules • Macros • Units • Digitize • Static Tools • Dynamic Tools • Drawing • Get Data Tools | |
| Aquaveo | ||