GMS:GMG Package: Difference between revisions
From XMS Wiki
Jump to navigationJump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
* Minimum damping (DLOW) | * Minimum damping (DLOW) | ||
* Maximum head change (CHGLIMIT) | * Maximum head change (CHGLIMIT) | ||
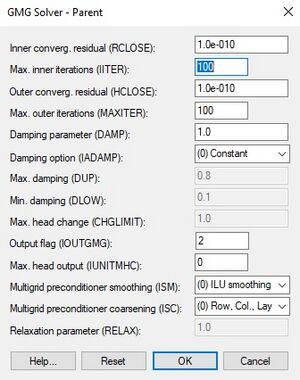
* Output flag (IOUTGMG) | * ''Output flag (IOUTGMG)'' – Flag that controls the output of the GMG solver. Values can be 0–4. | ||
** 0 = Only the solver inputs are printed. | |||
** 1 = For each linear solve, prints the number of PCG iterations, the value of the damping parameter, the l2-norm of the residual, and the maximum norm of the head change and its location (column, row, layer). At the end of a time/stress period, the total number of GMG calls, PCG iterations, and a running total of PCG iterations for all time/stress periods are printed. | |||
** 2 = The convergence history of the PCG iteration is printed, showing the l2-norm of the residual and the convergence factor for each iteration. | |||
** 3 = Same as 1 except the output is sent to the terminal instead of the output file. | |||
** 4 = Same as 2 except the output is sent to the terminal instead of the output file. | |||
* Maximum head output (IUNITMHC) | * Maximum head output (IUNITMHC) | ||
* Multi-grid preconditioner smoothing (ISM) | * Multi-grid preconditioner smoothing (ISM) | ||