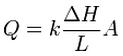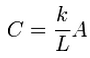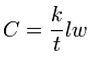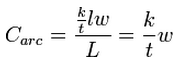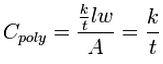GMS:Conductance: Difference between revisions
From XMS Wiki
Jump to navigationJump to search
| (16 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
Darcy's law states: | Darcy's law states: | ||
[[Image:eq_cond1. | [[Image:eq_cond1.png]] | ||
<!--{{hide in print| <math>\ Q=kiA</math>}}--> | <!--{{hide in print| <math>\ Q=kiA</math>}}--> | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
:''i'' = hydraulic gradient (unitless) | :''i'' = hydraulic gradient (unitless) | ||
:''A'' = gross cross-sectional area of flow [L^2]. | :''A'' = gross cross-sectional area of flow [L^2]. | ||
Darcy's law can also be expressed as: | Darcy's law can also be expressed as: | ||
[[Image:eq_cond2. | [[Image:eq_cond2.png]] | ||
<!--<math>\ Q=k \frac{\Delta H}{L} A</math>--> | <!--<math>\ Q=k \frac{\Delta H}{L} A</math>--> | ||
| Line 24: | Line 25: | ||
:''ΔH'' = the head loss [L] | :''ΔH'' = the head loss [L] | ||
:''L'' = the length of flow [L] | :''L'' = the length of flow [L] | ||
Since the unknown on the right side is the head, it is convenient to group all of the other terms together and call them conductance: | Since the unknown on the right side is the head, it is convenient to group all of the other terms together and call them conductance: | ||
[[Image:eq_cond3. | [[Image:eq_cond3.png]] | ||
<!--<math>\ Q=C \Delta H</math>--> | <!--<math>\ Q=C \Delta H</math>--> | ||
where: | where: | ||
: ''C'' = conductance [L^2/T] | : ''C'' = conductance [L^2/T] | ||
This results in the following general definition for conductance: | This results in the following general definition for conductance: | ||
[[Image:eq_cond4. | [[Image:eq_cond4.png]] | ||
<!--<math>\ C= \frac{k}{L} A</math>--> | <!--<math>\ C= \frac{k}{L} A</math>--> | ||
This may be represented more specifically in the following form. | This may be represented more specifically in the following form. | ||
[[Image:eq_cond5. | [[Image:eq_cond5.png]] | ||
<!--<math>\ C= \frac{k}{b} lw</math>--> | <!--<math>\ C= \frac{k}{b} lw</math>--> | ||
| Line 52: | Line 55: | ||
=== Arcs === | === Arcs === | ||
[[File:Arc-conductance.png|thumb|400 px|Arc conductance]] | |||
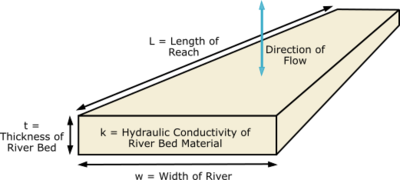
Fortunately, GMS can automatically calculate the lengths of arcs and areas of polygons. Therefore, when a conductance is entered for an [[GMS:Feature Objects#Arcs|arc]], it should be entered in terms of '''conductance per unit length'''. For example, in the case of rivers, conductance should be entered as: | Fortunately, GMS can automatically calculate the lengths of arcs and areas of polygons. Therefore, when a conductance is entered for an [[GMS:Feature Objects#Arcs|arc]], it should be entered in terms of '''conductance per unit length'''. For example, in the case of rivers, conductance should be entered as: | ||
[[Image:eq_cond6. | [[Image:eq_cond6.png]] | ||
<!--<math>\ C_{arc}= \dfrac{\tfrac{k}{t} lw}{L} = \frac{k}{t} w</math>--> | <!--<math>\ C_{arc}= \dfrac{\tfrac{k}{t} lw}{L} = \frac{k}{t} w</math>--> | ||
where: | |||
:''C<sub>arc</sub>'' = conductance per unit length [(L^2/T)/L] or [L/T] | |||
:''t'' = the thickness of the material [L] | |||
:''w'' = the width of the material along the length of the arc [L] | |||
When GMS applies the boundary condition from the arc to the grid cell, it automatically multiplies the entered value of conductance by the length of the arc that intersects the cell to create an accurate conductance value for the cell. | |||
=== Polygons === | === Polygons === | ||
For [[GMS:Feature Objects#Polygons|polygons]], conductance should be entered in a | For [[GMS:Feature Objects#Polygons|polygons]], conductance should be entered in a ''conductance per unit area'' form: | ||
[[Image:eq_cond7. | [[Image:eq_cond7.png]] | ||
<!--<math>\ C_{poly}= \dfrac{\tfrac{k}{t} lw}{A} = \frac{k}{t} </math>--> | <!--<math>\ C_{poly}= \dfrac{\tfrac{k}{t} lw}{A} = \frac{k}{t} </math>--> | ||
where: | |||
:''C<sub>poly</sub>'' = conductance per unit area [(L^2/T)/L^2] or [1/T] | |||
:''t'' = the thickness of the material [L] | |||
When GMS converts the stress from a polygon to a grid cell, it automatically multiplies the entered value of conductance by the area of the cell that is covered by the polygon to create an appropriate conductance value for the cell. This restores the dimensional accuracy to the expression for conductance. | |||
===Points=== | ===Points=== | ||
| Line 73: | Line 86: | ||
===Parameter Factors=== | ===Parameter Factors=== | ||
Beginning with GMS version 7.0, the Well, Drain, River, General head, and Stream boundary conditions have a parameter factor field that is associated with each boundary condition. The parameter factor is used with the parameter value to compute the final value of conductance for a given boundary condition (or in the case of the well package the final Q value). The parameter factor is automatically set by GMS when doing the | Beginning with GMS version 7.0, the Well, Drain, River, General head, and Stream boundary conditions have a parameter factor field that is associated with each boundary condition. The parameter factor is used with the parameter value to compute the final value of conductance for a given boundary condition (or in the case of the well package the final Q value). The parameter factor is automatically set by GMS when doing the '''Map→MODFLOW''' command. This value will be set to the length of the arc in the cell or the area of the polygon in the cell associated with the boundary condition; for a point feature the factor is set to 1.0. | ||
==See also== | |||
*[[GMS:Map to MODFLOW|Map to MODFLOW]] | |||
*[[GMS:MODFLOW Conceptual Model Approach|MODFLOW Conceptual Model Approach]] | |||
{{Navbox GMS}} | {{Navbox GMS}} | ||
[[Category:MODFLOW]] | [[Category:MODFLOW]] | ||
[[Category:Equations|Conductance]] | |||