GMS:GMG Package: Difference between revisions
From XMS Wiki
Jump to navigationJump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (13 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{MODFLOW Links}} | {{MODFLOW Links}} | ||
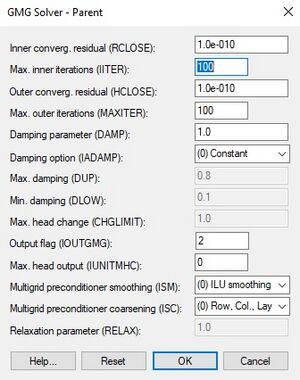
The GMG package is one of the [[GMS:MODFLOW Packages Supported in GMS#Solver Packages|solver packages]] for MODFLOW supported by GMS. The GMG solver is an iterative solver based on a multi-grid approach. | The GMG package is one of the [[GMS:MODFLOW Packages Supported in GMS#Solver Packages|solver packages]] for MODFLOW supported by GMS. The GMG solver is an iterative solver based on a multi-grid approach. | ||
Parameters include: | Parameters include: | ||
* ''Inner convergence residual (RCLOSE)'' – The algorithm computes the | * ''Inner convergence residual (RCLOSE)'' – The algorithm computes the 12-norm of the residual and compares it against RCLOSE. | ||
* ''Maximum inner iterations (IITER)'' – For each linear solution. The default is 100. Specify a smaller number for nonlinear problems to prevent an excessive number of inner iterations. | * ''Maximum inner iterations (IITER)'' – For each linear solution. The default is 100. Specify a smaller number for nonlinear problems to prevent an excessive number of inner iterations. | ||
* ''Outer convergence residual (HCLOSE)'' – For nonlinear problems. After each linear solve (inner iteration), the maximum norm of the head change is compared against HCLOSE. Can be set to a large number for linear problems. Ignored if ''Maximum outer iterations'' is 1. | * ''Outer convergence residual (HCLOSE)'' – For nonlinear problems. After each linear solve (inner iteration), the maximum norm of the head change is compared against HCLOSE. Can be set to a large number for linear problems. Ignored if ''Maximum outer iterations'' is 1. | ||
* ''Maximum outer iterations (MAXITER)'' – Also referred to as MXITER. For linear problems, set to 1. For nonlinear problems, set to a higher number though it is usually unnecessary to go above 100. | * ''Maximum outer iterations (MAXITER)'' – Also referred to as MXITER. For linear problems, set to 1. For nonlinear problems, set to a higher number though it is usually unnecessary to go above 100. | ||
* Damping parameter (DAMP) | * ''Damping parameter (DAMP)'' – A value of 1.0 should be used for linear problems. For nonlinear problems, a value less than 1.0 but greater than 0.0 may be necessary to achieve convergence. | ||
* Damping option (IADAMP) | * ''Damping option (IADAMP)'' – Flag that controls adaptive damping. Contains the following options: | ||
* Maximum damping (DUP) | <blockquote style="margin-top:0px; margin-bottom:0px;"> | ||
* Minimum damping (DLOW) | * "(0) Constant" | ||
* Maximum head change (CHGLIMIT) | * "(1) Cooley adaptive" | ||
* Output flag (IOUTGMG) | * "(2) RRR adaptive" | ||
* Maximum head output (IUNITMHC) | </blockquote> | ||
* Multi-grid preconditioner smoothing (ISM) | * ''Maximum damping (DUP)'' | ||
* Multi-grid preconditioner coarsening (ISC) | * ''Minimum damping (DLOW)'' | ||
* Relocation parameter (RELAX) | * ''Maximum head change (CHGLIMIT)'' | ||
* ''Output flag (IOUTGMG)'' – Flag that controls the output of the GMG solver. Values can be 0–4. | |||
<blockquote style="margin-top:0px; margin-bottom:0px;"> | |||
* 0 = Only the solver inputs are printed. | |||
* 1 = For each linear solve, prints the number of PCG iterations, the value of the damping parameter, the 12-norm of the residual, and the maximum norm of the head change and its location (column, row, layer). At the end of a time/stress period, the total number of GMG calls, PCG iterations, and a running total of PCG iterations for all time/stress periods are printed. | |||
* 2 = The convergence history of the PCG iteration is printed, showing the 12-norm of the residual and the convergence factor for each iteration. | |||
* 3 = Same as 1 except the output is sent to the terminal instead of the output file. | |||
* 4 = Same as 2 except the output is sent to the terminal instead of the output file. | |||
</blockquote> | |||
* ''Maximum head output (IUNITMHC)'' | |||
* ''Multi-grid preconditioner smoothing (ISM)'' – Flag that controls the type of smoother used in the multi-grid preconditioner. | |||
<blockquote style="margin-top:0px; margin-bottom:0px;"> | |||
* "(0) ILU smoothing" – This smoothing requires an additional vector on each multigrid level to store the pivots in the ILU factorization. | |||
* "(1) SGS smoothing" – Symmetric GaussSeidel (SGS) smoothing. | |||
</blockquote> | |||
* ''Multi-grid preconditioner coarsening (ISC)'' – Flag that controls semi-coarsening in the multi-grid preconditioner. | |||
<blockquote style="margin-top:0px; margin-bottom:0px;"> | |||
* "(0) Row, Col., Layer" – Coarsens all the rows, columns and layers. | |||
* "(1) Row, Col." – Coarsens all the rows and columns. | |||
* "(2) Col., Layer" – Coarsens all columns and layers. | |||
* "(3) Row, Layer" – Coarsens all rows and layers. | |||
* "(4) None" – No coarsening. | |||
</blockquote> | |||
* ''Relocation parameter (RELAX)'' – Used to improve the spectral condition number of the ILU preconditioned system. | |||
For more info on the GMG solver look at the following document: | For more info on the GMG solver look at the following document: | ||
:Wilson, John D., and Richard L. Naff. ''MODFLOW-2000, The US Geological Survey Modular Ground-Water Model | :Wilson, John D., and Richard L. Naff. ''MODFLOW-2000, The US Geological Survey Modular Ground-Water Model—GMG Linear Equation Solver Package Documentation.'' No. 2004-1261. 2004. [http://pubs.usgs.gov/of/2004/1261/] | ||
[[File:MODFLOW-GMG.jpg|thumb|none|center|300 px|The MODFLOW ''GMG Solver'' package dialog.]] | [[File:MODFLOW-GMG.jpg|thumb|none|center|300 px|The MODFLOW ''GMG Solver'' package dialog.]] | ||
| Line 30: | Line 53: | ||
[[Category:MODFLOW Dialogs]] | [[Category:MODFLOW Dialogs]] | ||
[[Category:External Links]] | [[Category:External Links]] | ||