WMS:GSSHA Contaminants: Difference between revisions
| Line 67: | Line 67: | ||
[[Category:GSSHA|C]] | [[Category:GSSHA|C]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:GSSHA Dialogs]] | ||
Revision as of 16:25, 3 December 2015
To model contaminants in GSSHA the contaminant transport option in the Job Control dialog must be turned on.
Contaminants are set up in three steps:
- Set up the contaminant types.
- Create the index maps for the contaminants.
- Set up the contaminant parameters in the mapping table.
Set up the contaminant types
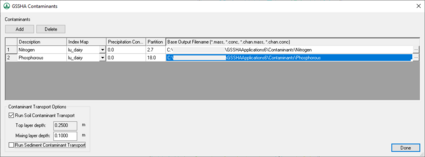
Contaminants are defined in the GSSHA Contaminants dialog, which is accessed either in the GSSHA menu or from the Job Control dialog. Click on Add to add new contaminants. Five parameters must be defined for each contaminant:
- A description of the contaminant.
- An index map showing the spatial distribution of the contaminant.
- The GSSHA output base filename for that contaminant.
- Concentration of the contaminant in rainfall.
- Soil water partition coefficient.
Note that the index map for each contaminant may be specified in the GSSHA Contaminants dialog or the GSSHA Index Map Table Editor dialog.
Create the index maps for the contaminants
The next step is to create index maps for the contaminants. These index maps are created in the same manner as other index maps and will usually be a cross between a soil type and a contaminant distribution coverage. However, there is no "Contaminant Distribution" coverage type in WMS. Simply create either a land use or soil type coverage and create polygons representing the different contaminant plumes. Different polygons for different initial concentrations of the contaminants will be useful later on as the specified contaminant concentration level for each index map ID (polygon) is a uniformly distributed concentration over the polygon. Also, in the coverage representing contaminants the entire grid must be covered by a polygon. Outside the contaminant plumes, the concentration will be zero.
When creating the index map from the coverages, a cross between a soil type and the contaminant distribution coverage will prove to meet the needs of the contaminant transport routines. The parameters that must be specified for each index map ID are a dispersion rate of the contaminant in standing water, a decay rate for the contaminant (first order kinetics), a cell uptake rate, and an initial mass loading. The contaminant distribution coverage should be used to define the initial mass loading and the soil type coverage should be used to define the cell uptake rate. The dispersion and decay rates will typically be uniform throughout the grid.
Set up the contaminant parameters in the mapping table
Finally, go to the GSSHA Index Map Table Editor. Choose one of the contaminants that have been set up and associate the correct index map with it. Follow the usual steps for setting up an index map and initialize each of the parameters for each ID.
Contaminant Parameters
- Dispersion rate ()
- Decay rate ()
- Cell uptake coefficient
- Initial mass loading (kg)
- Groundwater concentration (mg/l)
- Initial concentration (mg/l)
- Soil water distribution coefficient
- Max concentration/solubility (mg/l)
Related Topics
GSSHA | |
|---|---|
| XMS Wiki Links | Calibration (Automated • Manual • Output) • Channel Routing • Contaminants • Digital Dams • Embankment Arcs • Feature Objects (Arcs • Nodes • Polygons) • File Types • Groundwater • Groups • Hydraulic Structures • Job Control • Join SSURGO Data • Mapping Tables • Maps • Menu • Model Linkage • Multiple Simulations • Nutrients • Observations • Output Control • Overland Soil Erosion • Pipe and Node Parameters • Precipitation • Radar Rainfall • Save GSSHA Project File • Smooth GSSHA Streams • Snowmelt • Solution (Analysis • Data) |
| Related Tools | MWBM Wizard • Using Soil Type Data with GSSHA |
| GSSHA Wiki External Links | GSSHA Wiki: Overview • Primer • User's Manual • Tutorials |