WMS:GSSHA Mapping Tables
The GSSHA Map Table Editor dialog allows editing of the mapping tables for all of the spatially distributed parameters for options specified in the GSSHA Job Control dialog. The mapping tables relate parameter sets for each process to an index map that shows their spatial distribution.
There are tabs for each of these parameter sets. Some of the tabs require the option to have been turned on in the GSSHA Job Control dialog. If the tab is selected and the option has not been turned on there, a warning dialog will appear to ask if the option should be turned on.
The following buttons are always found at the bottom of the dialog, regardless of which tab is selected:
- Import Table... – Brings up the Open dialog where a CMT file (GSSHA Mapping Table File) can be selected and imported.
- Export Table... – Brings up the Enter the GSSHA Mapping Table file name dialog where the data from the selected tab can be exported as a CMT file.
- Job Control – Brings up the GSSHA Job Control dialog.
Roughness
The following options are available on this tab:
- Using index map – A drop-down listing all available index maps in the project. Select the desired index map from the list.
- Index map type – A drop-down list of index map types in the project. Select the desired type.
- Generate IDs – Generates a list of IDs from those found in the selected index map.
- Add ID – Adds a new ID to the spreadsheet, allowing manual creation of a new ID.
- Delete ID – Immediately deletes the selected ID.
The spreadsheet displays all of the IDs in the selected index map, one per column. It has the following rows:
- ID – A unique type ID.
- Description1 – An alphanumeric field. Enter a concise descriptive name for the ID type.
- Description2 – An optional alphanumeric field. Enter additional concise descriptive information.
- Surface roughness – A Manning's n value.
Roughness Exp
The following options are available on this tab:
- Using index map – A drop-down listing all available index maps in the project. Select the desired index map from the list.
- Generate IDs – Generates a list of IDs from those found in the selected index map.
- Add ID – Adds a new ID to the spreadsheet, allowing manual creation of a new ID.
- Delete ID – Immediately deletes the selected ID.
The spreadsheet displays all of the IDs in the selected index map, one per column. It has the following rows:
- ID – A unique type ID.
- Description1 – An alphanumeric field. Enter a concise descriptive name for the ID type.
- Description2 – An optional alphanumeric field. Enter additional concise descriptive information.
- Roughness exponent – An exponent value for depth-varying Manning/Strickler n value for the overland flow domain
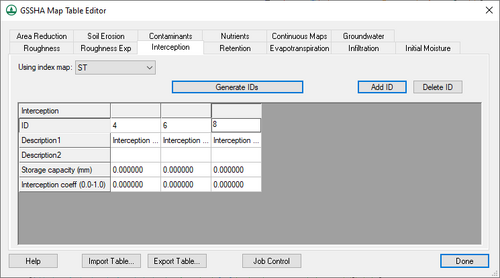
Interception
The following options are available on this tab:
- Using index map – A drop-down listing all available index maps in the project. Select the desired index map from the list.
- Generate IDs – Generates a list of IDs from those found in the selected index map.
- Add ID – Adds a new ID to the spreadsheet, allowing manual creation of a new ID.
- Delete ID – Immediately deletes the selected ID.
The spreadsheet displays all of the IDs in the selected index map, one per column. It has the following rows:
- ID – A unique type ID.
- Description1 – An alphanumeric field. Enter a concise descriptive name for the ID type.
- Description2 – An optional alphanumeric field. Enter additional concise descriptive information.
- Storage capacity – An initial quantity of rainfall (in millimeters) that is entirely intercepted by foliage.
- Interception coeff – A unitless number with a range between "0.0" and "1.0". This is the fraction of rainfall retained as intercepted water after satisfying the storage capacity.
Retention
The following options are available on this tab:
- Using index map – A drop-down listing all available index maps in the project. Select the desired index map from the list.
- Generate IDs – Generates a list of IDs from those found in the selected index map.
- Add ID – Adds a new ID to the spreadsheet, allowing manual creation of a new ID.
- Delete ID – Immediately deletes the selected ID.
The spreadsheet displays all of the IDs in the selected index map, one per column. It has the following rows:
- ID – A unique type ID.
- Description1 – An alphanumeric field. Enter a concise descriptive name for the ID type.
- Description2 – An optional alphanumeric field. Enter additional concise descriptive information.
- Retention depth – Specifies distributed retention depth (mm) over the index map.
Evapotranspiration
The following options are available on this tab:
- Using index map – A drop-down listing all available index maps in the project. Select the desired index map from the list.
- Generate IDs – Generates a list of IDs from those found in the selected index map.
- Add ID – Adds a new ID to the spreadsheet, allowing manual creation of a new ID.
- Delete ID – Immediately deletes the selected ID.
The spreadsheet displays all of the IDs in the selected index map, one per column. It has the following rows:
- ID – A unique type ID.
- Description1 – An alphanumeric field. Enter a concise descriptive name for the ID type.
- Description2 – An optional alphanumeric field. Enter additional concise descriptive information.
- Land-surface albedo – A dimensionless number with a range between "0.0" and "1.0". Fraction of radiation reflected back to the atmosphere.
- Vegetation height – Height of the vegetation in meters.
- Vegetation radiation coeff – A unitless number with a range between "0.0" and "1.0". Direct solar radiation penetrating the vegetation canopy and reaching the ground.
- Canopy stomatal resistance – Resistance of the canopy to transpiration at noon (s/m).
Infiltration
The following options are available on this tab:
- Using index map – A drop-down listing all available index maps in the project. Select the desired index map from the list.
- Generate IDs – Generates a list of IDs from those found in the selected index map.
- Add ID – Adds a new ID to the spreadsheet, allowing manual creation of a new ID.
- Delete ID – Immediately deletes the selected ID.
The spreadsheet displays all of the IDs in the selected index map, one per column. It has the following rows:
- ID – A unique type ID.
- Description1 – An alphanumeric field. Enter a concise descriptive name for the ID type.
- Description2 – An optional alphanumeric field. Enter additional concise descriptive information.
- Hydraulic conductivity – Typical value of "0.01" to "2.0", given in cm/hr. The saturated hydraulic conductivity, or Ks, is the rate at which water will enter the soil under unit head and saturated conditions.
- Capillary head – Typical value of "10.0" to "100.0", given in cm. The capillary suction head, or Ψf, is a measure of the combined adhesive forces that bind the water molecules to solid walls and the cohesive forces that attract water molecules to each other.
- Porosity – Also known as θs. The volume of voids/total volume of soil. A decimal fraction between "0.0" and "1.0", in m3/m3.
- Pore distribution index – The pore index value, λ, in cm/cm.
- Residual saturation – The water content of air dry soil, or θr. A decimal fraction between "0.0" and "1.0", in m3/m3.
- Field capacity – Also known as θf.
- Wilting point – A fraction between residual saturation and porosity (θwp), water content below which plants cannot uptake water from the soil.
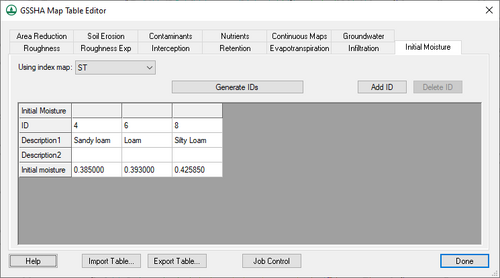
Initial Moisture
The following options are available on this tab:
- Using index map – A drop-down listing all available index maps in the project. Select the desired index map from the list.
- Generate IDs – Generates a list of IDs from those found in the selected index map.
- Add ID – Adds a new ID to the spreadsheet, allowing manual creation of a new ID.
- Delete ID – Immediately deletes the selected ID.
The spreadsheet displays all of the IDs in the selected index map, one per column. It has the following rows:
- ID – A unique type ID.
- Description1 – An alphanumeric field. Enter a concise descriptive name for the ID type.
- Description2 – An optional alphanumeric field. Enter additional concise descriptive information.
- Initial moisture – Also known as θi. A decimal fraction obtained by subtracting θs from θr, in m3/m3.
Area Reduction
The following options are available on this tab:
- Using index map – A drop-down listing all available index maps in the project. Select the desired index map from the list.
- Generate IDs – Generates a list of IDs from those found in the selected index map.
- Add ID – Adds a new ID to the spreadsheet, allowing manual creation of a new ID.
- Delete ID – Immediately deletes the selected ID.
The spreadsheet displays all of the IDs in the selected index map, one per column. It has the following rows:
- ID – A unique type ID.
- Description1 – An alphanumeric field. Enter a concise descriptive name for the ID type.
- Description2 – An optional alphanumeric field. Enter additional concise descriptive information.
- Impervious area fraction – Reduces the potential infiltration by the specified fraction. A unitless number with a range of "0.0" to "1.0".
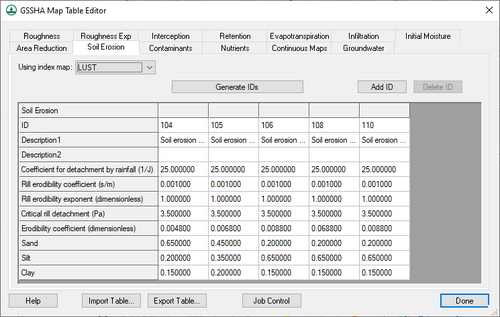
Soil Erosion
This tab requires the Soil erosion option be turned on in the GSSHA Job Control dialog. The following options are available on this tab:
- Using index map – A drop-down listing all available index maps in the project. Select the desired index map from the list.
- Generate IDs – Generates a list of IDs from those found in the selected index map.
- Add ID – Adds a new ID to the spreadsheet, allowing manual creation of a new ID.
- Delete ID – Immediately deletes the selected ID.
The spreadsheet displays all of the IDs in the selected index map, one per column. It has the following rows:
- ID – A unique type ID.
- Description1 – An alphanumeric field. Enter a concise descriptive name for the ID type.
- Description2 – An optional alphanumeric field. Enter additional concise descriptive information.
- Coefficient for detachment by rainfall – A function of rainfall intensity, or J-1, and determined by this equation: di = KI Cw CG Ci Iβ.
- Rill erodibility coefficient – A dimensionless number a in the equation shown here, expressed as s/m. Surface runoff detaches soil particles by exerting a shear stress that breaks the bonds between particles. Erosion in rills is lumped and described as gross rill erosion. Within a grid cell, rill erosion and flow are assumed to be uniformly distributed.
- Rill erodibility exponent – A dimensionless number b used in this equation.
- Critical rill detachment – Expressed as τ or "Pa" used in this equation.
- Erodibility coefficient – A dimensionless number K used in equation 108 here. A combined factor with a range of "0.0" to "1.0" that consists of the combined influence of soil erodibility, vegetation, and land-use.
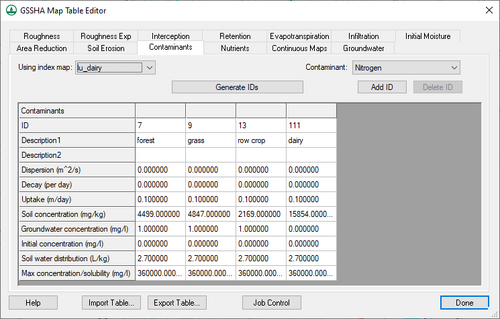
Contaminants
This tab requires the Contaminant transport option be turned on in the GSSHA Job Control dialog. The following options are available on this tab:
- Using index map – A drop-down listing all available index maps in the project. Select the desired index map from the list.
- Contaminant – A drop-down listing of all available contaminants in the project. Contaminants are defined in the GSSHA Contaminants dialog.
- Generate IDs – Generates a list of IDs from those found in the selected index map.
- Add ID – Adds a new ID to the spreadsheet, allowing manual creation of a new ID.
- Delete ID – Immediately deletes the selected ID.
The spreadsheet displays all of the IDs in the selected index map, one per column. It has the following rows:
- ID – A unique type ID.
- Description1 – An alphanumeric field. Enter a concise descriptive name for the ID type.
- Description2 – An optional alphanumeric field. Enter additional concise descriptive information.
- Dispersion – The overland dispersion coefficient, expressed in m2/s.
- Decay (per day) – The soil and overland decay coefficient.
- Uptake – The overland uptake coefficient, expressed in m/day.
- Soil concentration – The overland loading, expressed in mg/kg of soil.
- Groundwater concentration – The concentration of the contaminant in groundwater, expressed in mg/l of groundwater.
- Initial concentration – The initial concentration of the contaminant, expressed in mg/l.
- Soil water concentration – The soil water partition in the soil, expressed in mg/l of soil water.
- Max concentration/solubility – The maximum concentration (or solubility) of the contaminant, expressed in mg/l.
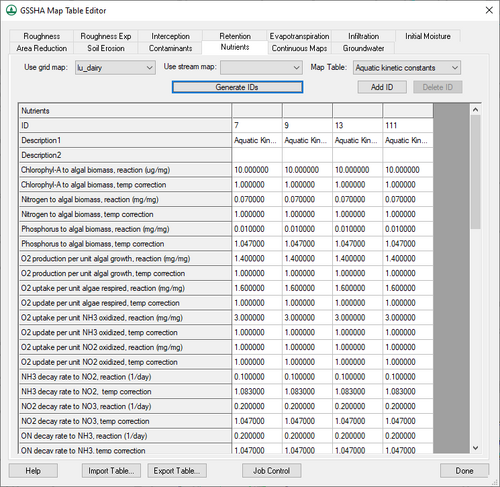
Nutrients
This tab requires the Nutrients option be turned on in the GSSHA Job Control dialog. The following options are available on this tab:
- Using index map – A drop-down listing all available index maps in the project. Select the desired index map from the list.
- Index map type – A drop-down listing of map types available. The option selected here affects what is shown in the Using index map drop-down. Select the desired map type from the list.
- Map Table – A drop-down listing all available map tables in the project. The option selected here affects what is shown in the spreadsheet section of this tab.
- "Aquatic kinetic constants"
- "Dispersion"
- "Nitrogen initial conditions"
- "Phosphorous initial conditions"
- "Carbon initial conditions"
- "Other initial conditions"
- "Dry bulk densities"
- "Soil nitrogen initial conditions"
- "Soil phosphorous initial conditions"
- "Soil carbon initial conditions"
- "Soil uptake rates"
- "Soil/water partitioning"
- "Groundwater nitrogen initial conditions"
- "Groundwater phosphorous initial conditions"
- "Groundwater other initial conditions"
- Generate IDs – Generates a list of IDs from those found in the selected index map.
- Add ID – Adds a new ID to the spreadsheet, allowing manual creation of a new ID.
- Delete ID – Immediately deletes the selected ID.
The spreadsheet displays all of the IDs in the selected index map, one per column. Depending on which options is selected in the Map Tables drop-down, the options change:
- "Aquatic kinetic constants" options
- ID – A unique type ID.
- Description1 – An alphanumeric field. Enter a concise descriptive name for the ID type.
- Description2 – An optional alphanumeric field. Enter additional concise descriptive information.
- Chlorophyl-A to algal biomass, reaction – Decimal value in ug/mg.
- Chlorophyl-A to algal biomass, temp correction – Decimal value.
- Nitrogen to algal biomass, reaction – Decimal value in mg/mg.
- Nitrogen to algal biomass, temp correction – Decimal value.
- Phosphorous to algal biomass, reaction – Decimal value in mg/mg.
- Phosphorous to algal biomass, temp correction – Decimal value.
- O2 production per unit algal biomass, reaction – Decimal value in mg/mg.
- O2 production per unit algal biomass, temp correction – Decimal value.
- O2 uptake per unit algae respired, reaction – Decimal value in mg/mg.
- O2 uptake per unit algae respired, temp correction – Decimal value.
- O2 uptake per unit NH3 oxidized, reaction – Decimal value in mg/mg.
- O2 uptake per unit NH3 oxidized, temp correction – Decimal value.
- O2 uptake per unit NO2 oxidized, reaction – Decimal value in mg/mg.
- O2 uptake per unit NO2 oxidized, temp correction – Decimal value.
- NH3 decay rate to NO2, reaction – Decimal value in 1/day.
- NH3 decay rate to NO2, temp correction – Decimal value.
- NO2 decay rate to NO3, reaction – Decimal value in 1/day.
- NO2 decay rate to NO3, temp correction – Decimal value.
- ON decay rate to NH3, reaction – Decimal value in 1/day.
- ON decay rate to NH3, temp correction – Decimal value.
- OP decay rate to DP, reaction – Decimal value in 1/day.
- OP decay rate to DP, temp correction – Decimal value.
- Carbonaceous deoxygenation rate constant, reaction – Decimal value in 1/day.
- Carbonaceous deoxygenation rate constant, temp correction – Decimal value.
- Reaeration coefficient, reaction – Decimal value in 1/day.
- Reaeration coefficient, temp correction – Decimal value.
- CBOD settling rate, reaction – Decimal value in 1/day.
- CBOD settling rate, temp correction – Decimal value.
- SOD (benthic oxygen) uptake, reaction – Decimal value in mg/ft2-day.
- SOD (benthic oxygen) uptake, temp correction – Decimal value.
- Algal growth rate, reaction – Decimal value in 1/day.
- Algal growth rate, temp correction – Decimal value.
- Algal respiration rate, reaction – Decimal value in 1/day.
- Algal respiration rate, temp correction – Decimal value.
- Algal settling rate, reaction – Decimal value in ft/day.
- Algal settling rate, temp correction – Decimal value.
- Benthos source rate for DP, reaction – Decimal value in mg/ft2-day.
- Benthos source rate for DP, temp correction – Decimal value.
- Benthos source rate for NH3, reaction – Decimal value in mg/ft2-day.
- Benthos source rate for NH3, temp correction – Decimal value.
- ON settling rate, reaction – Decimal value in 1/day.
- ON settling rate, temp correction – Decimal value.
- OP settling rate, reaction – Decimal value in 1/day.
- OP settling rate, temp correction – Decimal value.
- Michaelis-Menton half-saturation constant for light – Decimal value in Btu/(ft2-min).
- Michaelis-Menton half-saturation constant for nitrogen – Decimal value in mg/L.
- Michaelis-Menton half-saturation constant for phosphorous – Decimal value in mg/L.
- Algal preference factor for NH3 – Decimal value.
- Non-algal self-shading coefficient – Decimal value in 1/ft.
- Linear algal self-shading coeff – Decimal value in (1/ft)/(ug/L).
- Non-linear algal self-shading coeff – Decimal value in (1/ft)/(ug/L).
- Min DO levels for kinetics – Decimal value in mg/L.
- Dispersion coeff NO2 – Decimal value in m2/s.
- Dispersion coeff NO3 – Decimal value in m2/s.
- Dispersion coeff NH4 – Decimal value in m2/s.
- Dispersion coeff ON – Decimal value in m2/s.
- Dispersion coeff OP – Decimal value in m2/s.
- Dispersion coeff DP – Decimal value in m2/s.
- Dispersion coeff PO4 – Decimal value in m2/s.
- Dispersion coeff Algae – Decimal value in m2/s.
- Dispersion coeff CBOD – Decimal value in m2/s.
- Dispersion coeff DO – Decimal value in m2/s.
- "Dispersion" options
- ID – A unique type ID.
- Description1 – An alphanumeric field. Enter a concise descriptive name for the ID type.
- Description2 – An optional alphanumeric field. Enter additional concise descriptive information.
- Dispersion coefficient – A decimal field in m2/s.
- "Nitrogen initial conditions" options
- ID – A unique type ID.
- Description1 – An alphanumeric field. Enter a concise descriptive name for the ID type.
- Description2 – An optional alphanumeric field. Enter additional concise descriptive information.
- Nitrite, NO2 – A decimal field in mg/L.
- Nitrate, NO3 – A decimal field in mg/L.
- Ammonium, NH4 – A decimal field in mg/L.
- Organic nitrogen, ON – A decimal field in mg/L.
- "Phosphorous initial conditions" options
- ID – A unique type ID.
- Description1 – An alphanumeric field. Enter a concise descriptive name for the ID type.
- Description2 – An optional alphanumeric field. Enter additional concise descriptive information.
- Organic phosphorous, OP – A decimal field in mg/L.
- Dissolved phosphorous, DP – A decimal field in mg/L.
- Phosphate, PO4 – A decimal field in mg/L.
- "Carbon initial conditions" options
- ID – A unique type ID.
- Description1 – An alphanumeric field. Enter a concise descriptive name for the ID type.
- Description2 – An optional alphanumeric field. Enter additional concise descriptive information.
- Dissolved organic carbon, DOC – A decimal field in mg/L.
- Fraction organic carbon in DOC – A decimal field.
- "Other initial conditions" options
- ID – A unique type ID.
- Description1 – An alphanumeric field. Enter a concise descriptive name for the ID type.
- Description2 – An optional alphanumeric field. Enter additional concise descriptive information.
- Algae – A decimal field in mg/L.
- Carbonaceous biochemical oxygen demand, CBOD – A decimal field in mg/L.
- Dissolved oxygen, DO – A decimal field in mg/L.
- "Dry bulk densities" options
- ID – A unique type ID.
- Description1 – An alphanumeric field. Enter a concise descriptive name for the ID type.
- Description2 – An optional alphanumeric field. Enter additional concise descriptive information.
- Dry bulk density of mixing layer – A decimal field in kg/m3.
- Dry bulk density of second layer – A decimal field in kg/m3.
- Dry bulk density of bottom layer – A decimal field in kg/m3.
- "Soil nitrogen initial conditions" options
- ID – A unique type ID.
- Description1 – An alphanumeric field. Enter a concise descriptive name for the ID type.
- Description2 – An optional alphanumeric field. Enter additional concise descriptive information.
- NH4 Loading – A decimal field in g/kg.
- NO3 Loading – A decimal field in g/kg.
- Organic Active Nitrogen Loading – A decimal field in g/kg.
- Organic Stable Nitrogen Loading – A decimal field in g/kg.
- Organic Free Nitrogen Loading – A decimal field in g/kg.
- "Soil phosphorous initial conditions" options
- ID – A unique type ID.
- Description1 – An alphanumeric field. Enter a concise descriptive name for the ID type.
- Description2 – An optional alphanumeric field. Enter additional concise descriptive information.
- Mineral Active Phosphorous Loading – A decimal field in mg/kg.
- Mineral Soluble Phosphorous Loading – A decimal field in mg/kg.
- Mineral Stable Phosphorous Loading – A decimal field in mg/kg.
- Organic Active Phosphorous Loading – A decimal field in mg/kg.
- Organic Free Phosphorous Loading – A decimal field in mg/kg.
- Organic Stable Phosphorous Loading – A decimal field in mg/kg.
- "Soil carbon initial conditions" options
- ID – A unique type ID.
- Description1 – An alphanumeric field. Enter a concise descriptive name for the ID type.
- Description2 – An optional alphanumeric field. Enter additional concise descriptive information.
- Total soil organic carbon – A decimal field in kg/m2.
- Fraction total soil organic carbon in top (mixing) layer – A decimal field.
- Top layer organic active carbon fraction of total – A decimal field.
- Second/Third layer organic active carbon fraction of total – A decimal field.
- Fraction of organic active carbon that is dissolved – A decimal field.
- Fraction of organic stable carbon that is dissolved – A decimal field.
- "Soil uptake rates" options
- ID – A unique type ID.
- Description1 – An alphanumeric field. Enter a concise descriptive name for the ID type.
- Description2 – An optional alphanumeric field. Enter additional concise descriptive information.
- Mass uptake rate for NO2 from soil to overland – A decimal field in 1/day.
- Mass uptake rate for NO3 from soil to overland – A decimal field in 1/day.
- Mass uptake rate for NH4 from soil to overland – A decimal field in 1/day.
- Mass uptake rate for Organic Nitrogen from soil to overland – A decimal field in 1/day.
- Mass uptake rate for Organic Phosphorous from soil to overland – A decimal field in 1/day.
- Mass uptake rate for Dissolved Mineral Phosphorous from soil to overland – A decimal field in 1/day.
- "Soil/water partitioning" options
- ID – A unique type ID.
- Description1 – An alphanumeric field. Enter a concise descriptive name for the ID type.
- Description2 – An optional alphanumeric field. Enter additional concise descriptive information.
- Soil/Water partitioning coefficient for NO2 – A decimal field.
- Soil/Water partitioning coefficient for NO3 – A decimal field.
- Soil/Water partitioning coefficient for NH4 – A decimal field.
- Soil/Water partitioning coefficient for Organic Nitrogen – A decimal field.
- Soil/Water partitioning coefficient for Organic Phosphorous – A decimal field.
- Soil/Water partitioning coefficient for Dissolved Mineral Phosphorous – A decimal field.
- "Groundwater nitrogen initial conditions" options
- ID – A unique type ID.
- Description1 – An alphanumeric field. Enter a concise descriptive name for the ID type.
- Description2 – An optional alphanumeric field. Enter additional concise descriptive information.
- Concentration of NO2 in Groundwater – A decimal field in mg/L.
- Concentration of NO3 in Groundwater – A decimal field in mg/L.
- Concentration of NH4 in Groundwater – A decimal field in mg/L.
- Concentration of Organic Nitrogen in Groundwater – A decimal field in mg/L.
- "Groundwater phosphorous initial conditions" options
- ID – A unique type ID.
- Description1 – An alphanumeric field. Enter a concise descriptive name for the ID type.
- Description2 – An optional alphanumeric field. Enter additional concise descriptive information.
- Concentration of Organic Phosphorous in Groundwater – A decimal field in mg/L.
- Concentration of Dissolved Mineral Phosphorous in Groundwater – A decimal field in mg/L.
- Concentration of Phosphate (PO4) in Groundwater – A decimal field in mg/L.
- "Groundwater other initial conditions" options
- ID – A unique type ID.
- Description1 – An alphanumeric field. Enter a concise descriptive name for the ID type.
- Description2 – An optional alphanumeric field. Enter additional concise descriptive information.
- Concentration of CBOD in Groundwater – A decimal field in mg/L.
- Concentration of Dissolved Oxygen in Groundwater – A decimal field in mg/L.
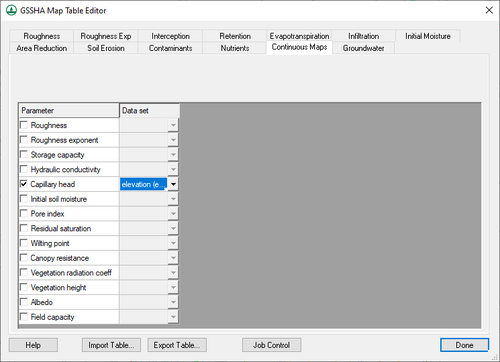
Continuous Maps
Each of the options on the tab can be turned on or off. The drop-down in the Dataset column lists all the "Continuous Maps" datasets in the project. The following options are available on this tab:
- Roughness
- Roughness exponent
- Storage capacity
- Hydraulic conductivity
- Capillary head
- Initial soil moisture
- Pore index
- Residual saturation
- Wilting point
- Canopy resistance
- Vegetation radiation coeff
- Vegetation height
- Albedo
- Field capacity
Groundwater
This tab requires the Groundwater option be turned on in the GSSHA Job Control dialog. The following options are available on this tab:
- Using index map – A drop-down listing all available index maps in the project. Select the desired index map from the list.
- Generate IDs – Generates a list of IDs from those found in the selected index map.
- Add ID – Adds a new ID to the spreadsheet, allowing manual creation of a new ID.
- Delete ID – Immediately deletes the selected ID.
The spreadsheet displays all of the IDs in the selected index map, one per column. It has the following rows:
- ID – A unique type ID.
- Description1 – An alphanumeric field. Enter a concise descriptive name for the ID type.
- Description2 – An optional alphanumeric field. Enter additional concise descriptive information.
- Hydraulic Conductivity – A value given in cm/hr. The saturated hydraulic conductivity, or Ks, is the rate at which water will enter the soil under unit head and saturated conditions.
- Porosity – The volume of voids/total volume of soil. A decimal fraction between "0.0" and "1.0", in m3/m3.
| [hide] GSSHA | |
|---|---|
| XMS Wiki Links | Calibration (Automated • Manual • Output) • Channel Routing • Contaminants • Digital Dams • Embankment Arcs • Feature Objects (Arcs • Nodes • Polygons) • File Types • Groundwater • Groups • Hydraulic Structures • Job Control • Join SSURGO Data • Mapping Tables • Maps • Menu • Model Linkage • Multiple Simulations • Nutrients • Observations • Output Control • Overland Soil Erosion • Pipe and Node Parameters • Precipitation • Radar Rainfall • Save GSSHA Project File • Smooth GSSHA Streams • Snowmelt • Solution (Analysis • Data) |
| Related Tools | MWBM Wizard • Using Soil Type Data with GSSHA |
| GSSHA Wiki External Links | GSSHA Wiki: Overview • Primer • User's Manual • Tutorials |
| [hide] WMS – Watershed Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | Terrain Data • Drainage • Map • Hydrologic Modeling • River • GIS • 2D Grid • 2D Scatter |  |
| Models: | CE-QUAL-W2 • GSSHA • HEC-1 • HEC-HMS • HEC-RAS • HSPF • MODRAT • NSS • OC Hydrograph • OC Rational • Rational • River Tools • Storm Drain • SMPDBK • SWMM • TR-20 • TR-55 | |
| Toolbars: | Modules • Macros • Units • Digitize • Static Tools • Dynamic Tools • Drawing • Get Data Tools | |
| Aquaveo | ||