WMS:Delineation with DEMs: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (7 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
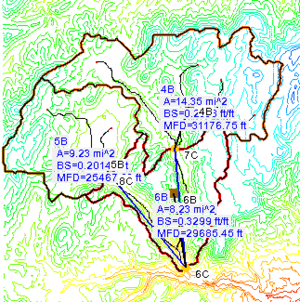
Watershed delineation with DEMs is one of the most common and simplest methods available for automatically characterizing a watershed. Many raster GIS programs have similar capabilities, but WMS has been designed specifically with the purpose of hydrologic and hydraulic modeling in mind | [[File:DelineatedDEM.png|thumb|300 px|Delineated DEM]] | ||
Watershed delineation with DEMs is one of the most common and simplest methods available for automatically characterizing a watershed. Many raster GIS programs have similar capabilities, but WMS has been designed specifically with the purpose of hydrologic and hydraulic modeling in mind. | |||
After defining basins with a DEM the results are converted to a drainage coverage for easier data storage and manipulation. It is also possible to [[WMS: | One program that has been developed for delineation on a DEM is the [[WMS:TOPAZ|TOPAZ]] program. A special version of TOPAZ has been created for use with WMS that only requires an elevation grid as input and produces a flow direction grid and a flow accumulation grid as outputs. | ||
The general process of delineating a DEM is as follows: | |||
#Obtain and import a DEM. | |||
#Compute flow directions and flow accumulations. | |||
#Identify the watershed outlet and covert DEM streams to arcs. | |||
#Define interior sub-basin outlets points. | |||
#Define basins. | |||
#Convert DEM basins to polygons. | |||
#Combute basin geometric data. | |||
More details about this process are given in the [[WMS:DEM Guidelines|DEM Guidelines]] article. | |||
DEM delineation can also be done using the [[WMS:Hydrologic Modeling Wizard Overview|''Hydrologic Modeling Wizard'']]. | |||
After defining basins with a DEM the results are converted to a drainage coverage for easier data storage and manipulation. It is also possible to [[WMS:DEM Basins|modify an existing delineation]] using [[WMS:Feature Objects|feature objects]]. | |||
==Related Topics== | ==Related Topics== | ||
| Line 7: | Line 22: | ||
* [[WMS:TOPAZ|TOPAZ]] | * [[WMS:TOPAZ|TOPAZ]] | ||
* [[WMS:Importing Flow Directions and Accumulations|Flow Directions and Flow Accumulations]] | * [[WMS:Importing Flow Directions and Accumulations|Flow Directions and Flow Accumulations]] | ||
* [[WMS:DEM | * [[WMS:DEM Basins|DEM Basins]] | ||
{{Template:WMSMain}} | {{Template:WMSMain}} | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:DEM|D]] | ||
{{stub}} | |||
Latest revision as of 21:52, 17 December 2019
Watershed delineation with DEMs is one of the most common and simplest methods available for automatically characterizing a watershed. Many raster GIS programs have similar capabilities, but WMS has been designed specifically with the purpose of hydrologic and hydraulic modeling in mind.
One program that has been developed for delineation on a DEM is the TOPAZ program. A special version of TOPAZ has been created for use with WMS that only requires an elevation grid as input and produces a flow direction grid and a flow accumulation grid as outputs.
The general process of delineating a DEM is as follows:
- Obtain and import a DEM.
- Compute flow directions and flow accumulations.
- Identify the watershed outlet and covert DEM streams to arcs.
- Define interior sub-basin outlets points.
- Define basins.
- Convert DEM basins to polygons.
- Combute basin geometric data.
More details about this process are given in the DEM Guidelines article.
DEM delineation can also be done using the Hydrologic Modeling Wizard.
After defining basins with a DEM the results are converted to a drainage coverage for easier data storage and manipulation. It is also possible to modify an existing delineation using feature objects.
Related Topics
WMS – Watershed Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | Terrain Data • Drainage • Map • Hydrologic Modeling • River • GIS • 2D Grid • 2D Scatter |  |
| Models: | CE-QUAL-W2 • GSSHA • HEC-1 • HEC-HMS • HEC-RAS • HSPF • MODRAT • NSS • OC Hydrograph • OC Rational • Rational • River Tools • Storm Drain • SMPDBK • SWMM • TR-20 • TR-55 | |
| Toolbars: | Modules • Macros • Units • Digitize • Static Tools • Dynamic Tools • Drawing • Get Data Tools | |
| Aquaveo | ||