WMS:GSSHA Job Control: Difference between revisions
From XMS Wiki
Jump to navigationJump to search
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
:[[Image:GsshaDepthVaryingRoughnessJobControl.png|thumb|none|left|500 px|GSSHA depth varying roughness option in the job control dialog]] | :[[Image:GsshaDepthVaryingRoughnessJobControl.png|thumb|none|left|500 px|GSSHA depth varying roughness option in the job control dialog]] | ||
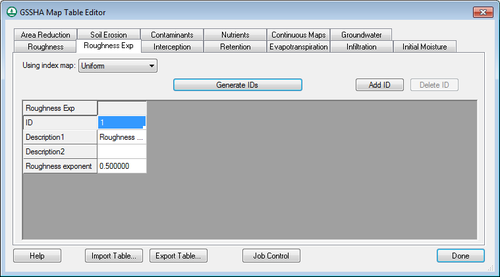
If this option is defined, | If this option is defined, define a mapping table specifying a depth-varying overland flow roughness exponent. This parameter is used in addition to the roughness mapping table, as shown below: | ||
:[[Image:GsshaDepthVaryingRoughnessIndexMap.png|thumb|none|left|500 px|GSSHA depth varying roughness table in the mapping table editor]] | :[[Image:GsshaDepthVaryingRoughnessIndexMap.png|thumb|none|left|500 px|GSSHA depth varying roughness table in the mapping table editor]] | ||
Revision as of 16:36, 5 February 2016
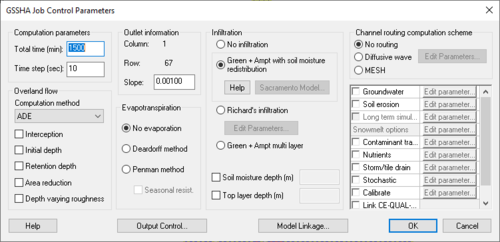
The GSSHA Job Control Parameters dialog is where options and data for computational processes in a GSSHA simulation are specified. The only required process, which is always included in every GSSHA simulation, is overland flow.
Computation Parameters (required)
- Total Time (min)
- Total time (simulation duration) / time step = total number of time steps. (e.g. 1440 min (total time) / 20 sec (time step) = 4320 computational time steps)
- Time Step (seconds)
- Choosing an appropriate time step is critical to the success of the simulation. If the time step used is too large then excessive numerical averaging will take place, delaying simulation flows and possibly causing oscillating results. Too small of a time step will take an inordinate amount of time for the simulation to run to completion.
- A time step that is evenly divisible into 60 sec must be chosen, i.e. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 10, 12, 15, 20, 30, or 60 seconds.
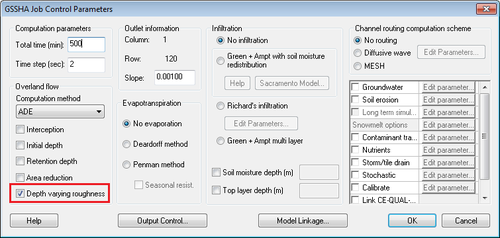
Depth Varying Roughness
There is an option in the GSSHA Job Control dialog to define a depth-varying overland flow roughness mapping table, as shown below:
If this option is defined, define a mapping table specifying a depth-varying overland flow roughness exponent. This parameter is used in addition to the roughness mapping table, as shown below:
Overland Flow
- Overland Flow Computation Method (required)
- The Explicit method is the fastest but least-robust method; the ADE-PC is the slowest, most-robust method
- Overland Flow Modifiers (optional)
- Rainfall Interception – specify the interception parameters using the Interception map table
- Initial Surface Water Depth – requires a continuous map of initial depths, which WMS does not currently write
- Surface Water Retention Depth – specify the retention depth using the Retention map table
- Areal Reduction of Retention Depth – WMS does not currently write the data that GSSHA requires for this option
Outlet Information (required)
- Outlet Cell Location (row, column) – WMS automatically computes these values
- Outlet Slope
Evapotranspiration (optional)
- Deardorff Formulation
- Penman-Montieth Formulation
Infiltration (optional)
- Green & Ampt
- Green & Ampt with Soil Moisture Redistribution
- Green & Ampt with a Long-Term Sacramento Soil Moisture Redistribution Function
- Richard's Formulation for Soil Moisture Redistribution and Groundwater Processes
Channel/Stream Flow Routing (optional)
- Diffusive Wave
- MESH
Other Processes/Options (optional)
- Groundwater (Subsurface)
- Soil Erosion
- Long-Term Simulation of ET, Soil Moisture Redistribution (using hydrometeorological data)
- Contaminant Transport
- Nutrients
- Storm/Tile Drains
- Stochastic – use this option to write stochastic parameter files
- Link CE-QUAL-W2 Output – use this option to write files linking CE-QUAL-W2 output to GSSHA
- Manage Files – use to manage the paths and filenames of all GSSHA input/output files
Related Topics
GSSHA | |
|---|---|
| XMS Wiki Links | Calibration (Automated • Manual • Output) • Channel Routing • Contaminants • Digital Dams • Embankment Arcs • Feature Objects (Arcs • Nodes • Polygons) • File Types • Groundwater • Groups • Hydraulic Structures • Job Control • Join SSURGO Data • Mapping Tables • Maps • Menu • Model Linkage • Multiple Simulations • Nutrients • Observations • Output Control • Overland Soil Erosion • Pipe and Node Parameters • Precipitation • Radar Rainfall • Save GSSHA Project File • Smooth GSSHA Streams • Snowmelt • Solution (Analysis • Data) |
| Related Tools | MWBM Wizard • Using Soil Type Data with GSSHA |
| GSSHA Wiki External Links | GSSHA Wiki: Overview • Primer • User's Manual • Tutorials |