GMS:PCGN Package
From XMS Wiki
| MODFLOW | |
|---|---|
| Pre-processing | |
| MODFLOW Commands | |
| Building a MODFLOW Model | |
| Map to MODFLOW | |
| Calibration | |
| Packages Supported in GMS | |
| Saving a MODFLOW Simulation | |
| Importing MODFLOW Files | |
| Unsupported MODFLOW Features | |
| Run MODFLOW | |
| Post-processing | |
| MODFLOW Display Options | |
| MODFLOW Post-Processing Viewing Options | |
| Reading a MODFLOW Simulation | |
| Tutorials | |
| Packages | |
| Flow: | BCF6, HUF, LPF, UPW |
| Solvers: | SMS |
| Other: | UZF1 |
The PCGN package or Preconditioned Conjugate Gradient Solver with Improved Nonlinear Control is one of the solvers available for MODFLOW-2005. Using the PCGN solver a specific GMS MODFLOW executable (mf2k5_..._parallel.exe) can be run with parallel processing on a single machine (though not across multiple machines on a network) greatly reducing run time.
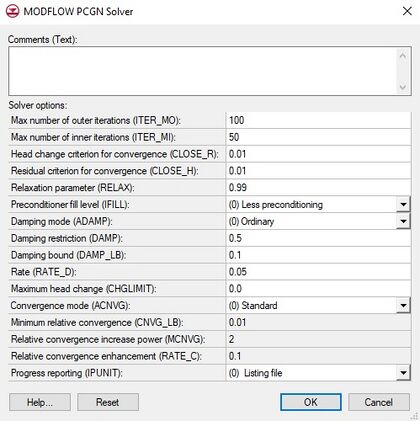
The MODFLOW PCGN Solver dialog has the following options:
- Comments (Text) – Allows up to 199 characters.
- Max number of outer iterations (ITER_MO) – For nonlinear problems, this variable must be set to some number greater than one, depending on the problem size and degree of nonlinearity. If set to 1, then the solver assumes that the problem is linear and the input requirements are greatly truncated.
- Max number of inner iterations (ITER_MI) – Set to some number greater than one, depending on the matrix size, degree of convergence called for, and the nature of the problem.
- Head change criterion for convergence (CLOSE_R) – If set to 1 then the problem will be linear. If set to be greater than 1 then it will be a nonlinear problem.
- Residual criterion for convergence (CLOSE_H) – Used as an alternate stopping criterion for the Picard iteration needed to solve a nonlinear problem.
- Relaxation parameter (RELAX) – Relaxation parameter for the modified incomplete Cholesky (MIC) preconditioner. Value can be between 0 and 1. Generally a value between 0.9 and 0.99 is advised for most problems.
- Preconditioner fill level (IFILL) – Fill level of the MIC preconditioner. Preconditioners with fill levels of 0 and 1 are available.
- (0) Less preconditioning
- (1) More preconditioning
- Damping mode (ADAMP) – Defines the mode of damping applied to the linear solution.
- (0) Ordinary – A constant value of damping parameter Θ = DAMP will be used.
- (1) Adaptive – Changes the damping parameter Θ in response to the difficulty the nonlinear solver encounters in solving a given problem.
- (2) Enhanced – The value of θ is increased (but never decreased) provided the Picard iteration is proceeding satisfactorily.
- Damping restriction (DAMP)
- Damping bound (DAMP_LB)
- Rate (RATE_D)
- Maximum head change (CHGLIMIT)
- Convergence mode (ACNVG)
- (0) Standard
- (1) Adaptive
- (2) Enhanced
- Minimum relative convergence (CNVG_LB)
- Relative convergence increase power (MCNVG)
- Relative convergence enhancement (RATE_C)
- Progress reporting (IPUNIT)
- (-1) None
- (0) Listing file
- (1) CSV file
For more information on this solver see the USGS documentation at http://water.usgs.gov/nrp/gwsoftware/modflow2000/MFDOC/pcgn.htm
| GMS – Groundwater Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | 2D Grid • 2D Mesh • 2D Scatter Point • 3D Grid • 3D Mesh • 3D Scatter Point • Boreholes • GIS • Map • Solid • TINs • UGrids | |
| Models: | FEFLOW • FEMWATER • HydroGeoSphere • MODAEM • MODFLOW • MODPATH • mod-PATH3DU • MT3DMS • MT3D-USGS • PEST • PHT3D • RT3D • SEAM3D • SEAWAT • SEEP2D • T-PROGS • ZONEBUDGET | |
| Aquaveo | ||
This article is a [stub]. You can help xmswiki by expanding it.
Hidden category: