GMS:SMS Package
From XMS Wiki
(Redirected from GMS:SMS Solver)
Jump to navigationJump to search
| MODFLOW | |
|---|---|
| Pre-processing | |
| MODFLOW Commands | |
| Building a MODFLOW Model | |
| Map to MODFLOW | |
| Calibration | |
| Packages Supported in GMS | |
| Saving a MODFLOW Simulation | |
| Importing MODFLOW Files | |
| Unsupported MODFLOW Features | |
| Run MODFLOW | |
| Post-processing | |
| MODFLOW Display Options | |
| MODFLOW Post-Processing Viewing Options | |
| Reading a MODFLOW Simulation | |
| Tutorials | |
| Packages | |
| Flow: | BCF6, HUF, LPF, UPW |
| Solvers: | SMS |
| Other: | UZF1 |
The Sparse Matrix Solver (SMS) Package is the only solver package compatible with MODFLOW-USG and is not compatible with other MODFLOW models.
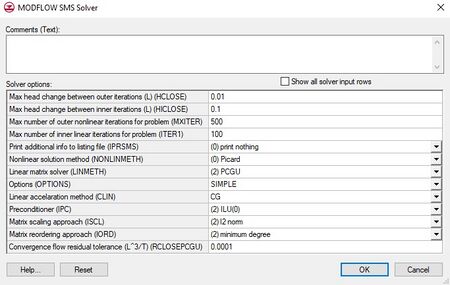
The MODFLOW SMS Solver dialog has the following options:
- Comments (Text) – Places a comment in the solver.
- Max head change between outer iterations (L)(HCLOSE)
- Max head change between inner iterations (L)(HICLOSE)
- Max number of outer nonlinear iterations for problem (MXITER)
- Max number of inner linear iterations for problem (ITER1)
- Print additional info to listing file (IPRSMS)
- (0) print nothing
- (1) print summary
- (2) print detail
- Nonlinear solution method (NONLINMETH)
- (-2) Picard with Cooley
- (-1) Picard with Delta-Bar-Delta
- (0) Picard
- (1) Newton with Delta-Bar-Delta
- (2) Newton and Cooley
- Linear matrix solver (LINMETH)
- (1) χMD
- (2) PCGU
- (3) SAMG
- Options (OPTIONS)
- SPECIFIED
- SIMPLE
- MODERATE
- COMPLEX
More information regarding inputs to the SMS package can be found in the MODFLOW-USG documentation at pubs.usgs.gov.
The SMS package, when used with GMS, also includes the option of using the SAMG or LMG within the SMS package. This option is selected under the Linear matrix solver (LINMETH) option in the MODFLOW SMS Solver dialog.
Nonlinear Solution Method Options
- Delta-bar-delta learning rate reduction factor (THETA)
- Delta-bar-delta learning rate increment (AKAPPA)
- Delta-bar-delta memory term factor (GAMA)
- Nonlinear fraction history added (AMOMENTUM)
- Maximum residual backtracking iterations (NUMTRACK)
- Residual change tolerance (BTOL)
- Residual change reduction size (BREDUC)
- Residual reduction limit (RESLIM)
χMD Options
- Acceleration method (IACL)
- (0) conjugate gradient
- (1) ORTHOMIN
- (2) Bi-CGSTAB
- Ordering scheme (NORDER)
- (0) original ordering
- (1) RCM ordering
- (2) minimum degree ordering
- ILU decomposition level of fill (LEVEL)
- Number of orthogonalizations for ORTHOMIN accel. (NORTH)
- Reduced system (IREDSYS)
- (0) do not apply
- (1) apply
- Residual tolerance criterion (RRCTOL)
- Perform drop tolerance (IDROPTOL)
- (0) do not perform
- (1) perform
- Drop tolerance value (EPSRN)
PCGU Options
- Linear acceleration method (CLIN)
- CG
- BCGS
- Preconditioner (IPC)
- (0) None
- (1) Jacobi
- (2) ILU(0)
- (3) MILU(0)
- Matrix scaling approach (ISCL)
- (0) None
- (1) POLCG preconditioner
- (2) l2 norm
- Matrix reordering approach (IORD)
- (0) Original
- (1) reverse Cuthill Mckee
- (2) minimum degree
- Convergence flow residual tolerance (L^3)(RCLOSEPCGU)
- MILU(0) relaxation factor (RELAXPCGU)
- Only solve active cells (SOLVEACTIVE)
- Bottom damping procedure used (DAMPBOT)
- Right-hand vector translated with linear solve (SHIFT)
- Truncated newton approach used (TRUNCATEDNEWTON)
| GMS – Groundwater Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | 2D Grid • 2D Mesh • 2D Scatter Point • 3D Grid • 3D Mesh • 3D Scatter Point • Boreholes • GIS • Map • Solid • TINs • UGrids | |
| Models: | FEFLOW • FEMWATER • HydroGeoSphere • MODAEM • MODFLOW • MODPATH • mod-PATH3DU • MT3DMS • MT3D-USGS • PEST • PHT3D • RT3D • SEAM3D • SEAWAT • SEEP2D • T-PROGS • ZONEBUDGET | |
| Aquaveo | ||
Retrieved from "https://www.xmswiki.com/index.php?title=GMS:SMS_Package&oldid=158294"