From XMS Wiki
This is the approved revision of this page, as well as being the most recent.
Jump to navigationJump to search
| 1. Start a new SMS project.
|
| 1. Start SMS, or clear existing projects in SMS.
|
- If SMS is already running, select File | Delete All.
- A new project can also be started by using CTRL + N.
|
|
| 2. Import data.
|
| 1. Gather and open image files.
|
Images are imported into the GIS module in SMS.
| 2. Import images from the web.
|
|
|
|
| 3. Review and edit the elevation data.
|
| 1. Review elevation data for errors.
|
| 1. Use the Dataset Info dialog.
|
- Find the "Z", "elevation" or "depth" datasets on the geometric object (mesh, TIN, grid, raster) that is being reviewed
- Right-click on elevation data and select Info.
- Review information in the Dataset Info dialog to see that the range of values are as expected.
|
| 2. Use contour display options.
|
- Turn off Points and Triangles, then turn on Contours in the Scatter tab of the Display Options dialog.
- Set contour options in the Contours tab. The "Color Fill" option is recommended for this.
- Look for inconsistent points (points with values much higher/lower than their neighbors or regions where no data points exist).
- Verify that the region being modeled is covered by the elevation/depth data and there are no holes.
|
| 3. Rotate the elevation data.
|
- Use the Rotate
 tool to examine the elevation data from different angles. tool to examine the elevation data from different angles.
|
|
| 2. Remove erroneous points and triangles.
|
- After reviewing the imported data, points or triangles covering regions where there are no data points should be deleted. This could include outlier points or thin triangles.
| 2. Manually remove points.
|
- Use Select Scatter Point
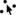 tool to select erroneous points in the scatter set. tool to select erroneous points in the scatter set.
- Review and edit point data in the Edit Window.
- Delete erroneous points.
|
|
| 3. Add breaklines.
|
- Select the Create Breakline
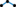 tool. tool.
- Click along points of a common elevation, such as at a bank toe or levee crest, to connect these points in the surface.
- Use the Backspace key to back up if an erroneous selection is made.
- Double-click or press Enter key to complete the breakline.
|
|
| 4. Define coastline.
|
| 1. Create an ADCIRC Boundary Conditions map coverage.
|
- Create a new coverage with the "ADCIRC Boundary Condition" type.
| 1. Create new coverage from scratch.
|
- Select Map Data in the Project Explorer and use the New Coverage right-click command.
- Use the New Coverage dialog to create a new coverage by selecting the desired coverage type, and naming the coverage.
|
| 2. Create new coverage from an existing coverage.
|
- Use the Duplicate command on an existing coverage. This will copy any feature objects on the coverage.
- Use the Rename command to give the coverage a new name.
- Change the coverage type.
|
|
| 2. Create the mainland arc.
|
| 1. Import an existing mainland arc. (optional)
|
- Use the File | Open command to import a coastline file containing a coastline arc.
- Right-click on the coastline arc using the Select Feature Arc
 tool and select the Attributes command. tool and select the Attributes command.
- Define the arc as a mainland arc in the ADCIRC Linear BC dialog.
|
| 2. Create a feature arc to use as a mainland.
|
1. Use the Create Feature Arc  tool to digitize the coastline. tool to digitize the coastline.
|
| 1. Create feature arcs, nodes and vertices.
|
- In the Map module, create feature objects in the active coverage.
- Use the Create Feature Arc
 tool to create arcs in the map coverage. tool to create arcs in the map coverage.
- Begin creating a new arc by clicking in the Graphics Window at either arc end. If clicking on an existing feature node, vertex or arc, the new arc will snap to that object.
- Double-click or press the Enter key to terminate the arc.
- Use the Create Feature Node
 tool to create additional nodes alone or to split arcs. tool to create additional nodes alone or to split arcs.
|
| 2. Modify arcs.
|
- Feature arcs often need to be edited after initial creation.
| 3. Split arcs.
|
- An existing arc can be split by:
| 2. Add a node the arc.
|
- Use the Create Feature Node
 tool to add a node on an arc in order to split it into two arcs. tool to add a node on an arc in order to split it into two arcs.
|
| 3. Add a new connecting arc.
|
- Use the Create Feature Arc
 tool to start or end a new arc on an existing arc to split the existing arc into two arcs. tool to start or end a new arc on an existing arc to split the existing arc into two arcs.
|
|
| 4. Merge arcs.
|
- Two arcs that share an end node can be merged together.
- Select the shared node using the Select Feature Node
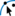 tool. tool.
- Right-click on the node and select the Convert to Vertex command to merge the arcs.
- If desired, the Select Feature Vertex
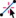 tool can be used to select and delete the new vertex. tool can be used to select and delete the new vertex.
|
|
|
| 2. Assign attributes to the mainland arc.
|
- Right-click on the coastline arc using the Select Feature Arc
 tool and select the Attributes command. tool and select the Attributes command.
- Define the arc as a mainland arc in the ADCIRC Linear BC dialog.
|
|
|
| 4. Assign ocean arc attributes.
|
- Right-click on the domain arc using the Select Feature Arc
 tool and select the Attributes command. tool and select the Attributes command.
- Define the arc in the ADCIRC Linear BC dialog.
|
| 5. Assign other boundary condition attributes. (optional)
|
1. Use the Create Feature Arc  tool to digitize the boundary condition arc. tool to digitize the boundary condition arc.
|
| 1. Create feature arcs, nodes and vertices.
|
- In the Map module, create feature objects in the active coverage.
- Use the Create Feature Arc
 tool to create arcs in the map coverage. tool to create arcs in the map coverage.
- Begin creating a new arc by clicking in the Graphics Window at either arc end. If clicking on an existing feature node, vertex or arc, the new arc will snap to that object.
- Double-click or press the Enter key to terminate the arc.
- Use the Create Feature Node
 tool to create additional nodes alone or to split arcs. tool to create additional nodes alone or to split arcs.
|
| 2. Modify arcs.
|
- Feature arcs often need to be edited after initial creation.
| 3. Split arcs.
|
- An existing arc can be split by:
| 2. Add a node the arc.
|
- Use the Create Feature Node
 tool to add a node on an arc in order to split it into two arcs. tool to add a node on an arc in order to split it into two arcs.
|
| 3. Add a new connecting arc.
|
- Use the Create Feature Arc
 tool to start or end a new arc on an existing arc to split the existing arc into two arcs. tool to start or end a new arc on an existing arc to split the existing arc into two arcs.
|
|
| 4. Merge arcs.
|
- Two arcs that share an end node can be merged together.
- Select the shared node using the Select Feature Node
 tool. tool.
- Right-click on the node and select the Convert to Vertex command to merge the arcs.
- If desired, the Select Feature Vertex
 tool can be used to select and delete the new vertex. tool can be used to select and delete the new vertex.
|
|
|
| 2. Assign attributes to the arc.
|
- Right-click on the boundary condition arc using the Select Feature Arc
 tool and select the Attributes command. tool and select the Attributes command.
- Define the arc with the desired boundary condition in the ADCIRC Linear BC dialog.
|
|
|
| 5. Create finite mesh functions.
|
| 1. Create shallow wavelength functions.
|
- Use the Data | Dataset Toolbox command
- Using the Coastal tool, create a celerity and wavelength functions. The following equation are used:
 . . . .
|
| 2. Create size functions.
|
| 1. General size function process.
|
| 3. Create mesh using the new size function dataset.
|
| 1. Create polygons in the map coverage.
|
- Polygons are not created automatically when arcs are enclosed. To create polygons:
- Use the Feature Objects | Build Polygons command.
|
| 2. Specify mesh type for each polygon (pave / patch / none).
|
| 2. Set the Mesh Type, Bathymetry Type, and Material Type for the polygon.
|
- Mesh types include Patch, Paving, Scalar Paving Density, and Constant Paving Density.
- Bathymetry type describes the elevation/topography source for the mesh nodes. Bathymetry types include a constant elevation value, interpolated elevation values from a scatter set, or interpolated elevation values from an existing mesh.
- Material types can be assigned to a polygon using materials previously created in Materials Data dialog.
|
| 3. Preview and edit the polygon mesh.
|
- Select the Preview Mesh button.
- Use the preview tools to edit the mesh.
- Set Arc Options to adjust distribution of vertices.
- Use Node Options to change how arcs are treated when using a patch mesh type.
|
|
|
|
| 2. Size function based on depth.
|
| 2. Use the Data Calculator to create a size function dataset based on depth.
|
- Use the Data | Dataset Toolbox command
- Using the Data Calculator, create a size function dataset based on depth. Use the following equation:

|
| 3. Create mesh using the new size function dataset.
|
| 1. Create polygons in the map coverage.
|
- Polygons are not created automatically when arcs are enclosed. To create polygons:
- Use the Feature Objects | Build Polygons command.
|
| 2. Specify mesh type for each polygon (pave / patch / none).
|
| 2. Set the Mesh Type, Bathymetry Type, and Material Type for the polygon.
|
- Mesh types include Patch, Paving, Scalar Paving Density, and Constant Paving Density.
- Bathymetry type describes the elevation/topography source for the mesh nodes. Bathymetry types include a constant elevation value, interpolated elevation values from a scatter set, or interpolated elevation values from an existing mesh.
- Material types can be assigned to a polygon using materials previously created in Materials Data dialog.
|
| 3. Preview and edit the polygon mesh.
|
- Select the Preview Mesh button.
- Use the preview tools to edit the mesh.
- Set Arc Options to adjust distribution of vertices.
- Use Node Options to change how arcs are treated when using a patch mesh type.
|
|
|
|
| 3. Size function based on slope.
|
| 2. Use the Data Calculator to create a size function dataset based on slope.
|
- Use the Data | Dataset Toolbox command
- Using the Data Calculator, create a size function dataset based on slope. Use the following equation:

|
| 3. Create mesh using the new size function dataset.
|
| 1. Create polygons in the map coverage.
|
- Polygons are not created automatically when arcs are enclosed. To create polygons:
- Use the Feature Objects | Build Polygons command.
|
| 2. Specify mesh type for each polygon (pave / patch / none).
|
| 2. Set the Mesh Type, Bathymetry Type, and Material Type for the polygon.
|
- Mesh types include Patch, Paving, Scalar Paving Density, and Constant Paving Density.
- Bathymetry type describes the elevation/topography source for the mesh nodes. Bathymetry types include a constant elevation value, interpolated elevation values from a scatter set, or interpolated elevation values from an existing mesh.
- Material types can be assigned to a polygon using materials previously created in Materials Data dialog.
|
| 3. Preview and edit the polygon mesh.
|
- Select the Preview Mesh button.
- Use the preview tools to edit the mesh.
- Set Arc Options to adjust distribution of vertices.
- Use Node Options to change how arcs are treated when using a patch mesh type.
|
|
|
|
| 4. Size function based on curvature.
|
| 2. Use the Data Calculator to create a size function dataset based on curvature.
|
- Use the Data | Dataset Toolbox command
- Using the Data Calculator, create a size function dataset based on curvature. Use the following equation:

|
| 3. Create mesh using the new size function dataset.
|
| 1. Create polygons in the map coverage.
|
- Polygons are not created automatically when arcs are enclosed. To create polygons:
- Use the Feature Objects | Build Polygons command.
|
| 2. Specify mesh type for each polygon (pave / patch / none).
|
| 2. Set the Mesh Type, Bathymetry Type, and Material Type for the polygon.
|
- Mesh types include Patch, Paving, Scalar Paving Density, and Constant Paving Density.
- Bathymetry type describes the elevation/topography source for the mesh nodes. Bathymetry types include a constant elevation value, interpolated elevation values from a scatter set, or interpolated elevation values from an existing mesh.
- Material types can be assigned to a polygon using materials previously created in Materials Data dialog.
|
| 3. Preview and edit the polygon mesh.
|
- Select the Preview Mesh button.
- Use the preview tools to edit the mesh.
- Set Arc Options to adjust distribution of vertices.
- Use Node Options to change how arcs are treated when using a patch mesh type.
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 6. Generate a mesh.
|
| 2. Create polygons in the ADCIRC coverage.
|
- Polygons are not created automatically when arcs are enclosed. To create polygons:
- Use the Feature Objects | Build Polygons command.
|
| 3. Specify mesh type for each polygon (pave / patch / none).
|
| 2. Set the Mesh Type, Bathymetry Type, and Material Type for the polygon.
|
- Mesh types include Patch, Paving, Scalar Paving Density, and Constant Paving Density.
- Bathymetry type describes the elevation/topography source for the mesh nodes. Bathymetry types include a constant elevation value, interpolated elevation values from a scatter set, or interpolated elevation values from an existing mesh.
- Material types can be assigned to a polygon using materials previously created in Materials Data dialog.
|
| 3. Preview and edit the polygon mesh.
|
- Select the Preview Mesh button.
- Use the preview tools to edit the mesh.
- Set Arc Options to adjust distribution of vertices.
- Use Node Options to change how arcs are treated when using a patch mesh type.
|
|
|
| 9. Review results.
|
| 1. Load solution files.
|
- The solution file should load after running the model assuming the Load Solution option was checked in the model wrapper before exiting the model run. If loading the solution file separately from the model run, do the following:
- Open the output files generated from the model run.
|
| 2. Review results datasets and data visualization.
|
| 1. Manually review dataset solutions.
|
- In the Project Explorer, click on solution dataset created from the simulation run and view results in the Graphics Window.
- Click through the time steps for each dataset to see changes over time in the Graphics Window.
|
| 2. Adjust the display options.
|
| 2. View display.
|
- Use the Rotate
 , Pan , Pan  , and Zoom , and Zoom  tools. tools.
- Use the View menu commands found in the Display menu.
- Use the Frame
 command to center and resize the display as needed. command to center and resize the display as needed.
|
| 3. Adjust display.
|
- Display may need to be adjusted during the remainder of the project.
- Use the Display Options dialog and viewing tools as needed.
- Use the Frame
 command to center and resize the display as needed. command to center and resize the display as needed.
|
|
| 3. Create a film loop visualization.
|
- Select a solution dataset and use the Data | Film Loop menu command.
- Use the Film Loop Setup wizard to specify the animation parameters.
- Save and view the animation file.
|
| 4. Create a plot.
|
| 1. Load solution files if not already in the project.
|
- The solution should load automatically assuming the Load Solution option was checked in the model wrapper before exiting the model run.
- If loading the solution separately from the model run, open the solution file generated from model run.
|
| 2. Create an observation coverage.
|
- Create a new coverage with the "Observation" type.
- Select Map Data in the Project Explorer and use the New Coverage right-click command.
- Use the New Coverage dialog to create a new coverage by selecting the desired coverage type, and naming the coverage.
|
| 3. Create observation points in the observation coverage.
|
| 1. Create feature arcs, nodes and vertices.
|
- In the Map module, create feature objects in the active coverage.
- Use the Create Feature Arc
 tool to create arcs in the map coverage. tool to create arcs in the map coverage.
- Begin creating a new arc by clicking in the Graphics Window at either arc end. If clicking on an existing feature node, vertex or arc, the new arc will snap to that object.
- Double-click or press the Enter key to terminate the arc.
- Use the Create Feature Node
 tool to create additional nodes alone or to split arcs. tool to create additional nodes alone or to split arcs.
|
| 2. Modify arcs.
|
- Feature arcs often need to be edited after initial creation.
| 3. Split arcs.
|
- An existing arc can be split by:
| 2. Add a node the arc.
|
- Use the Create Feature Node
 tool to add a node on an arc in order to split it into two arcs. tool to add a node on an arc in order to split it into two arcs.
|
| 3. Add a new connecting arc.
|
- Use the Create Feature Arc
 tool to start or end a new arc on an existing arc to split the existing arc into two arcs. tool to start or end a new arc on an existing arc to split the existing arc into two arcs.
|
|
| 4. Merge arcs.
|
- Two arcs that share an end node can be merged together.
- Select the shared node using the Select Feature Node
 tool. tool.
- Right-click on the node and select the Convert to Vertex command to merge the arcs.
- If desired, the Select Feature Vertex
 tool can be used to select and delete the new vertex. tool can be used to select and delete the new vertex.
|
|
|
| 4. Add observation point attributes.
|
- With the Select Feature Point
 tool, right-click on the observation point and select the Node Attributes command. tool, right-click on the observation point and select the Node Attributes command.
- Set the observation attributes in the Observation Coverage dialog.
|
| 5. Use the Plot Wizard to generate plot type.
|
- The Plot Wizard can generate any of the following plot types:
|
|
|
| 3. Use an observation profile plot.
|
| 1. Create an observation coverage.
|
- Create a new coverage with the "Observation" type.
- Select Map Data in the Project Explorer and use the New Coverage right-click command.
- Use the New Coverage dialog to create a new coverage by selecting the desired coverage type, and naming the coverage.
|
| 2. Create observation arcs in the observation coverage.
|
| 1. Create feature arcs, nodes and vertices.
|
- In the Map module, create feature objects in the active coverage.
- Use the Create Feature Arc
 tool to create arcs in the map coverage. tool to create arcs in the map coverage.
- Begin creating a new arc by clicking in the Graphics Window at either arc end. If clicking on an existing feature node, vertex or arc, the new arc will snap to that object.
- Double-click or press the Enter key to terminate the arc.
- Use the Create Feature Node
 tool to create additional nodes alone or to split arcs. tool to create additional nodes alone or to split arcs.
|
| 2. Modify arcs.
|
- Feature arcs often need to be edited after initial creation.
| 3. Split arcs.
|
- An existing arc can be split by:
| 2. Add a node the arc.
|
- Use the Create Feature Node
 tool to add a node on an arc in order to split it into two arcs. tool to add a node on an arc in order to split it into two arcs.
|
| 3. Add a new connecting arc.
|
- Use the Create Feature Arc
 tool to start or end a new arc on an existing arc to split the existing arc into two arcs. tool to start or end a new arc on an existing arc to split the existing arc into two arcs.
|
|
| 4. Merge arcs.
|
- Two arcs that share an end node can be merged together.
- Select the shared node using the Select Feature Node
 tool. tool.
- Right-click on the node and select the Convert to Vertex command to merge the arcs.
- If desired, the Select Feature Vertex
 tool can be used to select and delete the new vertex. tool can be used to select and delete the new vertex.
|
|
|
|
|



