Get Online Maps
Online maps are raster datasets that can contain imagery, elevation, or land use information. Online maps are imported as dynamic imagery—they will update when panning and zooming in or out of the Graphics Window. This requires that the XMS software have an active internet connection.
Online maps are accessed through the Get Online Maps ![]() macro (in GMS and WMS) or through the File | Add Online Maps menu command (in SMS).
macro (in GMS and WMS) or through the File | Add Online Maps menu command (in SMS).
Once the online maps command is activated, the Virtual Earth Map Locator dialog will appear, but only if no other dynamic images are in the project. In this dialog, the map location can be specified. See the section Virtual Earth Map Locator for more information on this dialog.
If a projection has not been set, or if the current projection is different than the selected map location, a warning dialog will appear asking for the projection to be set. The Display Projection dialog will then open. The projection of the map location will be entered as the default if available.
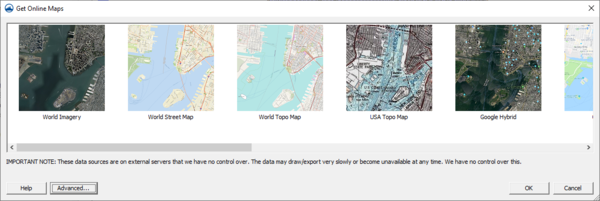
With the map location and projection set, the Get Online Maps dialog will appear. The Get Online Maps dialog allows selecting online data from a variety of different sources. Once online maps has been selected, the data resolution will be automatically adjusted based on the zoom parameters. Online maps can only be viewed in plan view.
Note that online data sources are on external servers that the XMS software has no control over. The data may draw/export very slowly or become unavailable at any time. The XMS software has no control over this.
More information about the various types of online data can be found by visiting the following links:
- World Imagery More Info
- World Street Maps More Info
- World Topo Maps More Info
- USA Topo Maps More Info
When online maps is available, right-click on each of the map items ![]() in the Project Explorer and select Export to convert them to static images that can be saved to the local hard drive. It is possible to convert or interpolate online maps containing elevation data to various elevation formats.
in the Project Explorer and select Export to convert them to static images that can be saved to the local hard drive. It is possible to convert or interpolate online maps containing elevation data to various elevation formats.
Exporting to a File
An online map can be exported to a file and loaded into the project. Do this if wanting to save a local copy and not be dependent on internet access. Two options exist for exporting:
- Export – This will export the online map as a raster file in TIF format. In doing this, the data will be resampled. See Resample Raster for more information.
- Export World File – Saves the world file data for the location. This will not include the image itself, only the projection information for a TIF file. A TIF file should be saved using the Export command.
With a static raster file there may be more commands and options available with a local file, such as interpolation or conversion to other object types, than with online maps.
Advanced Options
|
|
Please Note: Using the Advanced option requires very specific and detailed knowledge about the source data. If you need assistance with what to place in each field, you will need to contact the source data provider. Aquaveo is unable to provide any technical support beyond the documentation in this section. |
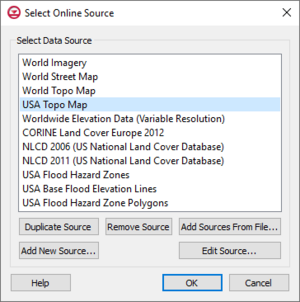
Clicking the Advanced button in the Get Online Maps dialog will bring up the Select Online Source dialog. A list of available sources is shown in this dialog. Sources can be added or edited through this dialog.
Options include:
- Duplicate Source – Creates a copy of the selected data source in the list above.
- Remove Source – Deletes the selected user-defined data source from the list above. Built-in sources cannot be removed.
- Add Sources from File – Brings up a browser where an online data source file (*.csv) can be selected to add a source to the available source list. When new data sources are added in the XMS software, a .csv file on your local computer is modified to include information on the new data source. The .csv files are saved in the user's "Roaming" directory (such as C:\Users\<username>\AppData\Roaming\Aquaveo\SMS 13.X) and can be copied from this directory, edited using a text editor, and passed to other users.
- Add New Source – Brings up the Add New Source dialog.
- Edit Source – Brings up the Add New Source dialog which allows editing an existing source. Built-in sources cannot be edited, but you can view information about the built-in data source and duplicate and edit the duplicated data source if desired.
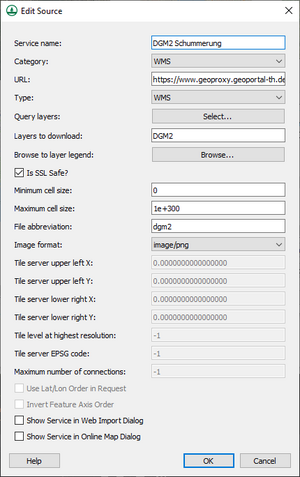
The Add New Source dialog is used when adding a new source and when editing an existing source. Before adding a new database as a source, the project location and projection should be set to a location that inside of the area covered by the source database.
The dialog has the following options:
- Service name – Allows entering or changing the name for the source.
- Category – Select the data source web service catagory. Can be Web Map Services (WMS), Web Feature Services (WFS), or Terrain Tile Services (TTS). WMS services are normally image data with Red, Green, and Blue bands unless the type of raster is an index map, in which case the WMS will download a single-band image with a lookup table to determine RGB values. WFS services download vector GIS data (point, arc, or polygon shapefiles). The only type of TTS service supported by XMS includes the Worldwide Elevation Data web service.
- URL – Specifies the URL of the data source. For a Web Map Service (WMS) data source, this is the location of the WMS service and includes the version number. For example, it might be in the format https://www.mrlc.gov/geoserver/mrlc_display/ows?service=wms&version=1.1.1 for a WMS service.
- Type – Specifies the type source for online data sources in the WMS category of services. The available options are ArcGIS REST (AGS), OGC Web Map Service (WMS), and Tile Map Service (TMS).
- Query layers – This shows a list of available layers from the web service. The layer can be selected from the list and, when you click the OK button, the layer information is entered into the Layers to download field.
- Layers to download – For sources containing layers (WMS and WFS), which layers to download can be specified here.
- Browse to layer legend – This button brings up a web page containing the legend for the specified web service.
- Is SSL Safe? – Check this if the data source server is SSL safe. This tells XMS to skip SSL certificate verification. This option may be needed if the server is using a self signed certificate. Many secure servers will require that this option is turned on.
- Minimum cell size – Sets a minimum cell size for data downloaded from the source. Data with cell sizes below this value will not be downloaded.
- Maximum cell size – Sets a maximum cell size for data downloaded from the source. Data with cell sizes above this value will not be downloaded.
- File abbreviation – Determines the file abbreviation that will be affixed to the file name when the file is downloaded from the web service.
- Image format – Determines the file format used to request data from the data source. The TIFF and PNG formats are available.
- Tile server upper left X – (only used for images downloaded with a WMS Category and TMS Type) The upper left X-coordinate of the tile server data, in the tile server's coordinate system.
- Tile server upper left Y – (only used for images downloaded with a WMS Category and TMS Type) The upper left Y-coordinate of the tile server data, in the tile server's coordinate system.
- Tile server lower right X – (only used for images downloaded with a WMS Category and TMS Type) The lower right X-coordinate of the tile server data, in the tile server's coordinate system.
- Tile server lower right Y – (only used for images downloaded with a WMS Category and TMS Type) The lower right Y-coordinate of the tile server data, in the tile server's coordinate system.
- Tile level at highest resolution – (only used for images downloaded with a WMS Category and TMS Type) The highest resolution tile level available for the specified TMS web service.
- Tile server EPSG code – (only used for images downloaded with a WMS Category and TMS Type) The EPSG code used by the TMS web service.
- Maximum number of connections – (only used for images downloaded with a WMS Category and TMS Type) Maximum number of simultaneous connections to the TMS web service.
- Use Lat/Lon Order in Request – (only used for data downloaded with a WFS Category) Whether to send the WFS request in Latitude (Y)/Longitude (X) order or Longitude (Y)/Latitude (X) order. If this option is turned on, the coordinates are sent to the WFS server in Latitude/Longitude order.
- Invert Feature Axis Order – (only used for data downloaded with a WFS Category) When data is downloaded from a WFS service, it is always converted to a shapefile before XMS reads the file. Sometimes, the X and Y coordinates are inverted in the WFS-downloaded data (the coordinates are listed in Lat/Lon order instead of the traditional Lon/Lat order) and the coordinates need to be inverted in the shapefile before being imported into XMS so the data shows up in the correct location. Turning this option on tells XMS to invert the axis order when converting the data to a shapefile.
- Show Service in Web Import Dialog – This option tells the XMS program to display the service in the web import (Data Service Options) dialog. The next time the Data Service Options dialog appears, this data source becomes available as an icon in the dialog.
- Show Service in Online Map Dialog – This option tells the XMS program to display the service in the Get Online Maps dialog. The option to make a map an online map is only available for data sources with WMS specified as the category.
Related Topics
| [hide] GMS – Groundwater Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | 2D Grid • 2D Mesh • 2D Scatter Point • 3D Grid • 3D Mesh • 3D Scatter Point • Boreholes • GIS • Map • Solid • TINs • UGrids | |
| Models: | FEFLOW • FEMWATER • HydroGeoSphere • MODAEM • MODFLOW • MODPATH • mod-PATH3DU • MT3DMS • MT3D-USGS • PEST • PHT3D • RT3D • SEAM3D • SEAWAT • SEEP2D • T-PROGS • ZONEBUDGET | |
| Aquaveo | ||
| [hide] SMS – Surface-water Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | 1D Grid • Cartesian Grid • Curvilinear Grid • GIS • Map • Mesh • Particle • Quadtree • Raster • Scatter • UGrid |  |
| General Models: | 3D Structure • FVCOM • Generic • PTM | |
| Coastal Models: | ADCIRC • BOUSS-2D • CGWAVE • CMS-Flow • CMS-Wave • GenCade • STWAVE • WAM | |
| Riverine/Estuarine Models: | AdH • HEC-RAS • HYDRO AS-2D • RMA2 • RMA4 • SRH-2D • TUFLOW • TUFLOW FV | |
| Aquaveo • SMS Tutorials • SMS Workflows | ||
| [hide] WMS – Watershed Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | Terrain Data • Drainage • Map • Hydrologic Modeling • River • GIS • 2D Grid • 2D Scatter |  |
| Models: | CE-QUAL-W2 • GSSHA • HEC-1 • HEC-HMS • HEC-RAS • HSPF • MODRAT • NSS • OC Hydrograph • OC Rational • Rational • River Tools • Storm Drain • SMPDBK • SWMM • TR-20 • TR-55 | |
| Toolbars: | Modules • Macros • Units • Digitize • Static Tools • Dynamic Tools • Drawing • Get Data Tools | |
| Aquaveo | ||