Lidar: Difference between revisions
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
:* '''''Note:''''' Currently WMS does not support this feature. | :* '''''Note:''''' Currently WMS does not support this feature. | ||
; Interpolate to Raster : Lidar data can be used to create a new [[GMS:Rasters|raster]]. Unlike lidar, rasters are uniformly gridded data. Since rasters can also be used as a source of interpolation, it can be useful to convert the lidar to a raster that | ; Interpolate to Raster : Lidar data can be used to create a new [[GMS:Rasters|raster]]. Unlike lidar, rasters are uniformly gridded data. Since rasters can also be used as a source of interpolation, it can be useful to convert the lidar to a raster that is more manageable and then use the raster for interpolation thereafter. | ||
:All lidar points lying within each raster cell are averaged to determine the value for that raster cell. | :All lidar points lying within each raster cell are averaged to determine the value for that raster cell. | ||
Revision as of 17:54, 26 May 2021
Lidar data is surveying data created by taking measurements with pulsed laser light. Lidar data can be used in XMS software for display and interpolation. Lidar is typically used to get elevation data for use in a model.
Lidar files typically have a *.las or *.laz extension. The *.laz extension is simply a compressed *.las file. XMS software can read both types of files. When a lidar file is opened it appears in the Project Explorer with this icon ![]() under GIS Layers.
under GIS Layers.
Lidar Display Options
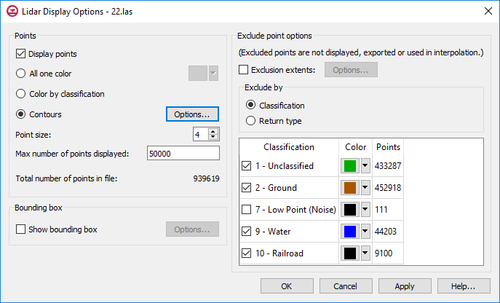
The Lidar Display Options dialog can be accessed by right-clicking on the lidar object in the Project Explorer. Note that currently this is the only way to access the Lidar Display Options dialog and that the main Display Options dialog does not include lidar options. Each lidar object has its own display options which can be set independently of other lidar files’ display options.
The left side of the dialog shows options for displaying points and a bounding box, and the right side shows options for excluding points.
Point Color
- Lidar points can be colored all the same color, or according to their classification, or by using contour options. The lidar contour options are the same as contour options used elsewhere in XMS, except that the only Color Method available is "Color Fill".
Max number of points displayed
- Because lidar data is typically quite large, in order to speed up the display of lidar points, the maximum number of lidar points displayed can be set to something less than the total number of points in the file. Points will be sampled based on the order that they appear in the file and the exclusion options.
Bounding box
- A bounding box can be displayed showing the XYZ extents of the data.
Exclude point options
- The right side of the Lidar Display Options dialog shows options used to exclude points. Excluding points is often helpful due to the sheer quantity of lidar data. Excluded points are not displayed, exported, or used when interpolating.
- Lidar points may be excluded by XYZ extents as well as by either classification or lidar return type.
Exclusion extents
- If the Exclusion extents option is turned on, an Options button is enabled that, when clicked, opens the Lidar Exclusion Extents dialog. This dialog allows for a minimum and maximum XYZ range to be specified. All points outside this range will be excluded. The XY range, or the Z range, or both can be used to exclude points. If the XY range is being used to exclude points, and if the display is currently in plan view, an option is available to update the minimum and maximum XY range using the current view. Selecting the Update button causes the bounds of the current view to be copied to the table.
Classifications and Return types
- Lidar files typically include data on point classifications and return types. This data can be used to exclude points.
- Exclude by classification
- If the Classification option is selected in the Exclude by section, a table shows all the classifications found in the file. Only checked classifications will be included. If Color by classification is chosen (under Points on the left of the dialog), a color can be specified for each classification and those colors will be used in the display. The Points column in the table gives the total number of points for each classification. By default, low point noise is excluded when opening a lidar file.
- Exclude by return type
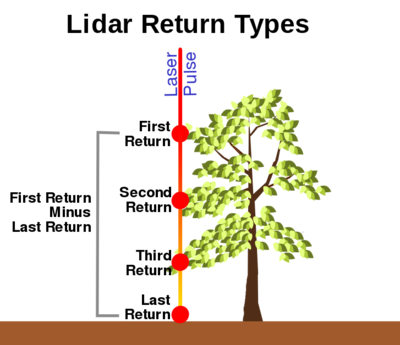
- If the Return type option is selected, the table shows four possible return types. The following figure illustrates what is meant by a lidar “return”.
- Each lidar point includes two numbers related to the laser pulse: the total number of returns, and the points’ return number. A return type is a combination of these two numbers. XMS currently lists four return types that may be useful when excluding points:
- If the Return type option is selected, the table shows four possible return types. The following figure illustrates what is meant by a lidar “return”.
- Single and Last-of-many – This is actually two return types, both of which imply the last point, which is typically the ground surface.
- First-of-many – Typically some feature above the ground, such as a tree top, or even a bird.
- Second but not-last – Typically lower vegetation. Not the ground.
- First – Could be anything, as it may also be the last point.
- A point may be included in more than one return type, for example, a first point would be included in 2, first-of-many, and 4, first.
Lidar Interpolation
Lidar can be interpolated to other data types. Commands to interpolate a lidar file are found in the right-click menu.
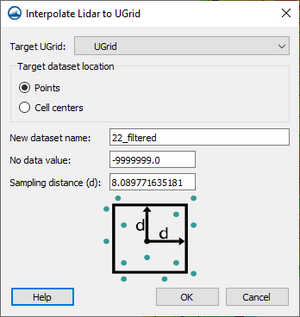
- Interpolate to UGrids
- One or more lidar files can be interpolated to a UGrid points or cell centers to create a new dataset. The lidar points lying within a square defined by a sampling distance are averaged to provide a data value that is then assigned to the UGrid point or cell.
- If there are sparse areas in the lidar that would potentially leave “holes” in the dataset, GMS will attempt to fill these holes by interpolating from the surrounding cells. If the hole is not completely surrounded by cells with valid interpolated values, cells in the hole will be assigned the No data value.
- Note: Currently WMS does not support this feature.
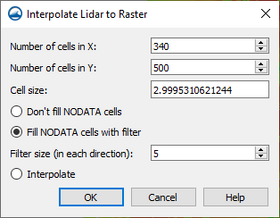
- Interpolate to Raster
- Lidar data can be used to create a new raster. Unlike lidar, rasters are uniformly gridded data. Since rasters can also be used as a source of interpolation, it can be useful to convert the lidar to a raster that is more manageable and then use the raster for interpolation thereafter.
- All lidar points lying within each raster cell are averaged to determine the value for that raster cell.
- Sparse areas in the lidar that could lead to “holes” in the raster are treated similarly to holes when interpolating to UGrids.
Merging Lidar Files
Multiple files can be merged into one file. This is done by selecting the lidar files in the Project Explorer, right-clicking, and selecting the Merge command. All the lidar files to be merged must have the same projection.
Since each lidar file has its own display options, merging multiple lidar files into one can make it simpler to change the display options for all of the data.
Lidar Commands
Lidar commands are found by right-clicking on a lidar file in the Project Explorer. The menu contains many of the standard commands. Unique commands to lidar files includes:
- Display Options
- Opens the Lidar Display Options dialog where options for displaying lidar data can be set. This is the only way to reach this dialog at this time.
- Interpolate to Raster
- Opens the Interpolate Lidar to Raster dialog to create a new raster file.
- Interpolate to UGrid
- Opens the Interpolate Lidar to UGrid dialog to creates a new dataset under a UGrid using the lidar values.
- Convert to 2D Scatter
- Creates a 2D scatter set from the lidar elevation data.
- Merge
- Combines multiple selected lidar files into one lidar file.
- Properties
- Brings up a Properties dialog which displays information about the lidar file.
Related Topics
GMS – Groundwater Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | 2D Grid • 2D Mesh • 2D Scatter Point • 3D Grid • 3D Mesh • 3D Scatter Point • Boreholes • GIS • Map • Solid • TINs • UGrids | |
| Models: | FEFLOW • FEMWATER • HydroGeoSphere • MODAEM • MODFLOW • MODPATH • mod-PATH3DU • MT3DMS • MT3D-USGS • PEST • PHT3D • RT3D • SEAM3D • SEAWAT • SEEP2D • T-PROGS • ZONEBUDGET | |
| Aquaveo | ||
SMS – Surface-water Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | 1D Grid • Cartesian Grid • Curvilinear Grid • GIS • Map • Mesh • Particle • Quadtree • Raster • Scatter • UGrid |  |
| General Models: | 3D Structure • FVCOM • Generic • PTM | |
| Coastal Models: | ADCIRC • BOUSS-2D • CGWAVE • CMS-Flow • CMS-Wave • GenCade • STWAVE • WAM | |
| Riverine/Estuarine Models: | AdH • HEC-RAS • HYDRO AS-2D • RMA2 • RMA4 • SRH-2D • TUFLOW • TUFLOW FV | |
| Aquaveo • SMS Tutorials • SMS Workflows | ||
WMS – Watershed Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | Terrain Data • Drainage • Map • Hydrologic Modeling • River • GIS • 2D Grid • 2D Scatter |  |
| Models: | CE-QUAL-W2 • GSSHA • HEC-1 • HEC-HMS • HEC-RAS • HSPF • MODRAT • NSS • OC Hydrograph • OC Rational • Rational • River Tools • Storm Drain • SMPDBK • SWMM • TR-20 • TR-55 | |
| Toolbars: | Modules • Macros • Units • Digitize • Static Tools • Dynamic Tools • Drawing • Get Data Tools | |
| Aquaveo | ||