GMS:Standard MODFLOW Parameters: Difference between revisions
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
===Editing=== | ===Editing=== | ||
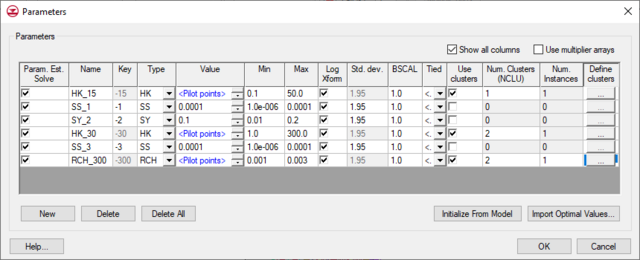
When GMS reads a model that uses standard MODFLOW parameters it converts them to regular GMS key value approach parameters. The parameters can then be edited using the Parameters Dialog. Recharge, evapotranspiration, LPF, and HUF parameters are special in that you can edit the instance and cluster information associated with these types of parameters. | When GMS reads a model that uses standard MODFLOW parameters it converts them to regular GMS key value approach parameters. The parameters can then be edited using the ''Parameters'' Dialog. Recharge, evapotranspiration, LPF, and HUF parameters are special in that you can edit the instance and cluster information associated with these types of parameters. | ||
==MODFLOW Parameter Clusters Dialog== | ==MODFLOW Parameter Clusters Dialog== | ||
Revision as of 16:30, 18 May 2012
| MODFLOW | |
|---|---|
| Pre-processing | |
| MODFLOW Commands | |
| Building a MODFLOW Model | |
| Map to MODFLOW | |
| Calibration | |
| Packages Supported in GMS | |
| Saving a MODFLOW Simulation | |
| Importing MODFLOW Files | |
| Unsupported MODFLOW Features | |
| Run MODFLOW | |
| Post-processing | |
| MODFLOW Display Options | |
| MODFLOW Post-Processing Viewing Options | |
| Reading a MODFLOW Simulation | |
| Tutorials | |
| Packages | |
| Flow: | BCF6, HUF, LPF, UPW |
| Solvers: | SMS |
| Other: | UZF1 |
| Caution
There are two ways to do MODFLOW parameterization in GMS:
The "key value" approach is the preferred approach to defining parameters in GMS. Using key values is the only option for WEL, RIV, DRT, DRN, GHB, CHD, STR, and HFB parameters. In GMS, using the key value approach with these parameters provides the same functionality of parameter instances available in MODFLOW. Key values can also be used with array based parameters. However, GMS does support defining array based parameters with clusters and instances (for ETS, EVT, RCH parameters). When reading in a MODFLOW simulation that was created outside of GMS all parameters will be converted to key values so long as the parameter can be represented by key values. Key values can not be used to represent an array based parameter if the parameter is defined using more than one cluster or more than one instance. Also, if more than one parameter uses the same zone array with a matching IZ value then the parameter can not be represented using key values. Further, if the multiplier array associated with the parameter has values other than 1.0 in the zones where the parameter is used then the parameter can not be represented with key values. The standard MODFLOW method is considered an "advanced" feature in GMS. Only users that understand how MODFLOW uses parameters should attempt to use this feature. |
This article describes how to use the standard MODFLOW parameterization method in GMS.
Contents
Support in GMS
Reading
GMS can read MODFLOW models that use standard MODFLOW parameters.
Writing
GMS writes MODFLOW models using the key value approach. So, although GMS can read models that use standard MODFLOW parameters, it cannot write them using the standard MODFLOW parameter method. Writing is usually done using the key value method. There are a few exceptions which include recharge and evapotranspiration parameter instances, and LPF and HUF parameter clusters. GMS will write these parameters using the standard MODFLOW parameter method because these cannot always be represented using the key value method.
Editing
When GMS reads a model that uses standard MODFLOW parameters it converts them to regular GMS key value approach parameters. The parameters can then be edited using the Parameters Dialog. Recharge, evapotranspiration, LPF, and HUF parameters are special in that you can edit the instance and cluster information associated with these types of parameters.
MODFLOW Parameter Clusters Dialog
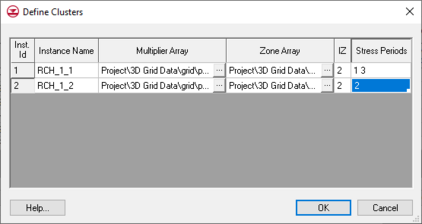
The MODFLOW Parameter Clusters Dialog allows users to define instances for RCH, EVT, LPF, and HUF parameters that use clusters. The inputs in this dialog basically follow the necessary inputs for defining a parameter instance in a package file. You may wish to review the MODFLOW Parameter Clusters and Instances section below.
Array based parameters are defined using clusters. A cluster is a multiplier array, a zone array, and specified zone values where the parameter is applied. Multiplier arrays and zone arrays have associated data sets underneath the three dimensional grid in the Project Explorer.
Instances are enabled for RCH and EVT parameters. Instances allow the user to define multiple sets of clusters that are all tied to one parameter. Then the user may use different instances in different stress periods in their MODFLOW model. For more information on parameter instances consult the MODFLOW documentation.
In the MODFLOW Parameters dialog the user selects the "Define clusters" option for a parameter. This will allow the user to specify the number of instances and clusters that are used to define the parameter.
In the Parameter Instances dialog the user defines a name for each parameter instance for RCH and EVT parameters. For LPF parameters a level is defined and for HUF parameters a hyrdogeologic unit is defined. Then for each cluster the user selects a multiplier array and a zone array. These are data sets on the 3D Grid. The user must also specify the zone values (IZ) where the parameter is to be applied in the model. If there is more than one IZ value for the cluster then the user enters the numbers with spaces between the entries. So if the parameter is to be applied where the zone array values are 1 and 3 then the user would enter "1 3". The user must also specify the stress periods where an instance is to be used. The numbers entered in the Stress Periods field should also be space delimited. This means if you want an instance to be used in stress periods 1, 2, and 5 then your entry in the Stress Periods field should be "1 2 5".
When the package is written out for MODFLOW the instances will be included in the parameter definition and used for forward runs or for parameter estimation runs.
MODFLOW Parameter Clusters and Instances
For those wanting to follow the standard MODFLOW approach to parameterization, the following explanation may be helpful. You should refer to the MODFLOW documentation for more information.
Definitions
Here is a brief review of the most important terms used when dealing with parameters.
- Parameter - Has a name, type, one or more clusters, and zero or more instances.
- Parval - The value of the parameter.
- Cluster - Has a multiplier array (Mltarr), a zone array (Zonarr), and zone numbers (IZ).
- Mltarr - Name of the multiplier array. Parval is multiplied by this to define the value.
- Zonarr - Name of the zone array used to define the cells that are associated with a parameter.
- IZ - Up to 10 zone numbers (separated by spaces) that define the cells that are associated with a parameter.
- Instance - Parameter cluster that could be used for different stress periods in a MODFLOW simulation.
Examples
Below are some examples showing different ways parameters can be used. The examples use parameters to define recharge for a forward run (not doing inverse modeling). The grid in the examples is 5 rows, 5 columns, 1 layer. The examples use the following multiplier and zone arrays.
Multiplier arrays
| MULT0001 | MULT0002 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Zone Arrays
| ZONE0001 | ZONE0002 | ZONE0003 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Example 1
Steady state. 1 recharge parameter with 1 cluster, 1 instance.
| Recharge file | Variables | Explanations |
|---|---|---|
PARAMETER 1 3 40 Param1 RCH 0.00005 1 MULT0001 ZONE0001 2 1 1 Param1 |
PARAMETER NPRCH NRCHOP IRCHCB PARNAM PARTYP Parval NCLU Mltarr Zonarr IZ INRECH INIRCH Pname |
One recharge parameter will be used Apply to highest active cell, save CCF to unit 40 Parameter name, type, value and number of clusters Multiplier array, zone array, and zone number One parameter used in current stress period, INIRCH (ignored) Name of parameter used to define RECH in this stress period |
Results
The resulting recharge applied to the top-most active layer would be:
| 0.00005 | 0.00005 | 0.00005 | 0 | 0 |
| 0.00005 | 0.00005 | 0.00005 | 0 | 0 |
| 0.00005 | 0.00005 | 0.00005 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Example 2
Steady state. 2 recharge parameters:
- the first with 1 cluster, 1 instance
- the second with 2 clusters, 1 instance.
| Recharge file | Variables | Explanations |
|---|---|---|
PARAMETER 2 3 40 Param1 RCH 0.00005 1 MULT0001 ZONE0001 2 Param2 RCH 0.00004 2 MULT0002 ZONE0002 4 5 MULT0002 ZONE0003 6 7 2 1 Param1 Param2 |
PARAMETER NPRCH NRCHOP IRCHCB PARNAM PARTYP Parval NCLU Mltarr Zonarr IZ PARNAM PARTYP Parval NCLU Mltarr Zonarr IZ Mltarr Zonarr IZ INRECH INIRCH Pname Pname |
Two recharge parameters will be used Apply to highest active cell, save CCF to unit 40 Parameter name, type, value and number of clusters Multiplier array, zone array, and zone number Parameter name, type, value and number of clusters Multiplier array, zone array, and zone numbers Multiplier array, zone array, and zone numbers Two parameters used in current stress period, INIRCH (ignored) Name of parameter used to define RECH in this stress period Name of parameter used to define RECH in this stress period |
Results
The intermediate results for each parameter cluster are listed below:
| Param1 | Param2, cluster 1 | Param2, cluster 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
The final result after accumulating each cluster is:
| 0.00005 | 0.00005 | 0.00005 | 0 | 0 |
| 0.00005 | 0.00005 | 0.00007 | 0.00002 | 0 |
| 0.00007 | 0.00007 | 0.00009 | 0.00004 | 0.00002 |
| 0.00002 | 0.00002 | 0.00002 | 0.00002 | 0.00002 |
| 0.00002 | 0.00002 | 0.00002 | 0.00002 | 0.00002 |
Example 3
Transient. 1 recharge parameter with 1 cluster, 2 instances. One instance is used in the first and third stress periods, and the other is used in the second stress period.
| Recharge file | Variables | Explanations |
|---|---|---|
PARAMETER 1 3 40 Param1 RCH 0.00005 1 INSTANCES 2 Instance1 MULT0001 ZONE0001 2 Instance2 MULT0002 ZONE0001 2 1 1 Param1 Instance1 1 1 Param1 Instance2 1 1 Param1 Instance1 |
PARAMETER NPRCH NRCHOP IRCHCB PARNAM PARTYP Parval NCLU INSTANCES NUMINST INSTNAM Mltarr Zonarr IZ INSTNAM Mltarr Zonarr IZ INRECH INIRCH Pname Iname INRECH INIRCH Pname Iname INRECH INIRCH Pname Iname |
One recharge parameters will be used Apply to highest active cell, save CCF to unit 40 Parameter name, type, value number of clusters, number of instances Instance name Multiplier array, zone array, and zone number Instance name Multiplier array, zone array, and zone number One parameters used in current stress period, INIRCH (ignored) Name of parameter and name of instance used in this stress period One parameters used in current stress period, INIRCH (ignored) Name of parameter and name of instance used in this stress period One parameters used in current stress period, INIRCH (ignored) Name of parameter and name of instance used in this stress period |
Results
The intermediate results for each parameter cluster are listed below:
Stress Period 1, Param1, Instance RCH_1_1
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Stress Period 2, Param1, Instance RCH_1_2
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Stress Period 3, Param1, Instance RCH_1_1
|
| GMS – Groundwater Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | 2D Grid • 2D Mesh • 2D Scatter Point • 3D Grid • 3D Mesh • 3D Scatter Point • Boreholes • GIS • Map • Solid • TINs • UGrids | |
| Models: | FEFLOW • FEMWATER • HydroGeoSphere • MODAEM • MODFLOW • MODPATH • mod-PATH3DU • MT3DMS • MT3D-USGS • PEST • PHT3D • RT3D • SEAM3D • SEAWAT • SEEP2D • T-PROGS • ZONEBUDGET | |
| Aquaveo | ||