WMS:GSSHA Job Control
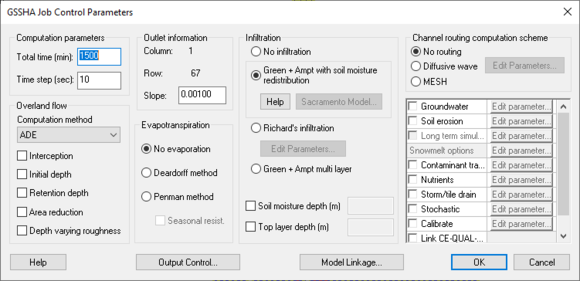
The GSSHA Job Control Parameters dialog contains options and data for computational processes in a GSSHA simulation. The only required process, which is always included in every GSSHA simulation, is overland flow.
There are five buttons at the bottom of the dialog:
- Help – Opens this page in a web browser.
- Output Control... – Opens the GSSHA Output Control dialog.
- Model Linkage... – Opens the GSSHA Model Linkage dialog.
- OK – Saves all changes made and exits the GSSHA Job Control Parameters dialog.
- Cancel – Discards all changes made and exits the GSSHA Job Control Parameters dialog.
Computation Parameters
The Computation parameters section is required and has the following options:
- Total time (min) – An integer giving the total duration of the simulation in minutes.
- Time step (sec) – An integer giving the duration of each time step in the simulation in seconds. The time step must be evenly divisible into 60 seconds (e.g., 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 10, 12, 15, 20, 30, or 60 seconds).
The total number of time steps is determined by dividing the total time by the time step. For example, for a simulation with a total time of 1440 minutes and with a time step of 20 seconds, there would be 4320 total computational time steps. Choosing an appropriate time step is critical to the success of the simulation. If the time step used is too large, excessive numerical averaging will take place, delaying simulation flows and possibly causing oscillating results. Too small of a time step causes the simulation to take an inordinate amount of time to run to completion.
Overland Flow
The Overland flow section has the following options:
- Computation method – A drop-down with the following options:
- "Explicit" – Completes most quickly, but is the least robust method.
- "ADE" – Alternating Direction Explicit method.
- "ADE-PC" – Alternating Direction Explicit Predictor-Corrector method. Completes most slowly, but is the most robust.
- Interception – Turn on to specify the rainfall interception parameters using the Interception map table.
- Initial depth – If turned on, requires a continuous map of initial surface water depths, which WMS does not currently write.
- Retention depth – Turn on to specify the surface water retention depth using the Retention map table.
- Area reduction – If turned on, requires a table listing areal reduction of retention depth, which WMS does not currently write.
- Depth varying roughness – If turned on, allows defining of a depth-varying overland flow Roughness map table. If this option is turned on, a depth-varying overland flow Roughness exponent must also be defined.
Outlet Information
The Outlet information section has the following options:
- Column – An integer automatically computed by WMS representing the total number of columns in each raster map. Not user editable.
- Row – An integer automatically computed by WMS representing the total number of rows in each raster map. Not user editable.
- Slope – The slope of the cell containing the watershed outlet. This must be a positive decimal number.
Evapotranspiration
The Evapotranspiration section has the following options:
- No evaporation – Select to not calculate any evapotranspiration.
- Deardorff method – Select to calculate evapotranspiration using the Deardorff formula.
- Penman method – Select to calculate evapotranspiration using the Penman-Montieth formula.
- Seasonal resist. – Turn on to calculate canopy stomatal resistance of the canopy to transpiration at noon (s/m).
Infiltration
The Infiltration section has the following options:
- No infiltration – Select to not calculate any infiltration.
- Green + Ampt with soil moisture redistribution – Useful for simulating multiple rainfall events in a series.
- Help – Opens the Infiltration:Parameter Estimates page on the GSSHA Wiki.
- Sacramento Model... – Opens the SAC-SMA Model dialog.
- Richard's infiltration –
- Edit Parameters... – Opens the Richard's Parameters dialog.
- Green + Ampt multi-layer – Used for modeling varying soil conditions through different layers.
- Soil moisture depth (m) – Tells how deep the moisture penetrates. A decimal depth value in meters.
- Top layer depth (m) – Tells how deep the top layer of soil is. A decimal depth value in meters.
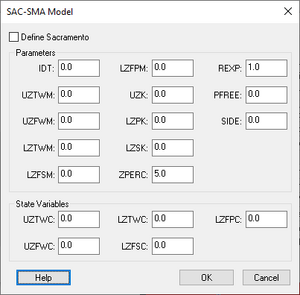
SAC-SMA Model Dialog
This dialog is only accessible when Long term simulation is turned on in the other parameters section of the GSSHA Job Control Parameters dialog. When that option is turned on, select Green + Ampt with soil moisture redistribution in the Infiltration section and click Sacramento Model....
The SAC-SMA Model dialog has the following options:
- Define Sacramento
- Parameters section
- IDT –
- UZTWM – Maximum upper zone tension water (mm)
- UZFWM – Maximum upper zone free water (mm)
- LZTWM – Maximum lower zone tension water (mm)
- LZFSM – Maximum lower zone free water, secondary (mm)
- LZFPM – Maximum lower zone free water, primary (mm)
- UZK – Upper zone recession coefficient
- LZPK – Lower zone recession coefficient, primary
- LZSK – Lower zone recession coefficient, secondary
- ZPERC – Minimum percolation rate coefficient
- REXP – Percolation equation exponent
- PRFREE – Percent percolating directly to lower zone free water (percent in decimal)
- SIDE – Portion of the baseflow which does not go to the stream (percent in decimal)
- State Variables section
- UZTWC – Upper zone tension water contents
- UZFWC – Upper zone free water contents
- LZTWC – Lower zone tension water contents
- LZFSC – Lower zone free primary zone contents
- LZFPC – Lower zone free supplemental zone contents
At the bottom are three buttons:
- Help – Opens this section on this page in a web browser.
- OK – Saves all changes made and exits the SAC-SMA Model dialog.
- Cancel – Discards all changes made and exits the SAC-SMA Model dialog.
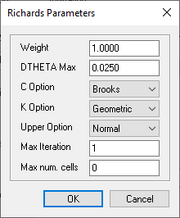
Richard's Parameters Dialog
The Richard's Paramters dialog has the following options:
- Weight – Fraction between 0.0 and 1.0 (dimensionless).
- D THETA Max – The maximum allowable water content change in any finite difference cell during a single time-step. A positive decimal value. Default is 0.025.
- C Option – Sets the curves used to define the relationships between water content and soil suction, pressure, and water content and hydraulic conductivity. A drop-down with the following options:
- "Brooks" – Method for estimating relative hydraulic activity.
- "Havercamp" – Method for calculating relative hydraulic activity.
- K Option – The method used to calculate inter-cell hydraulic conductivities. Choose from the drop-down with the following options:
- "Geometric" – Geometric average.
- "Arithmetic" – Arithmetic weighting of values.
- Upper Option – Method used to determine the hydraulic conductivity at the soil surface during ponded water conditions. A drop-down with the following options:
- "Normal" – Specifies that the normal cell-centered value of hydraulic conductivity be used.
- "Green Ampt" – Specifies that the saturated hydraulic conductivity of the soil in the cell be used.
- "Average" – Specifies that an average of the two other options be used.
- Max Iteration – An integer value for the maximum number of iteration.
- Max num. cells – An integer value for the maximum number of cells.
At the bottom are two buttons:
- OK – Saves all changes made and exits the Richard's Paramters dialog.
- Cancel – Discards all changes made and exits the Richard's Paramters dialog.
Channel Routing Computation Scheme
The Channel routing computation scheme section has the following options:
- No routing –
- Diffusive Wave – Clicking Edit Parameters... brings up the GSSHA Channel Routing Parameters dialog.
- MESH –
Other Parameters
The other parameters section is not labelled and has the following options:
- Groundwater – Turn on and click Edit parameters... to bring up the GSSHA Groundwater dialog.
- Soil erosion – Turn on and click Edit parameters... to bring up the Overland soil erosion dialog.
- Long term simulation – Turn on and click Edit parameters... to bring up the Long Term Simulation dialog.
- Snowmelt options – Click Edit parameters... to bring up the GSSHA Snowmelt Options dialog.
- Contaminant transport – Turn on and click Edit parameters... to bring up the GSSHA Contaminants dialog.
- Nutrients – Turn on and click Edit parameters... to bring up the Nutrients dialog.
- Storm/tile drain – Turn on and click Edit parameters... to bring up the Storm/tile drain dialog.
- Stochastic – Turn on and click Edit parameters... to bring up the GSSHA Batch Mode/Stochastics dialog.
- Calibrate – Turn on and click Edit parameters... to bring up the Parameters dialog.
- Link CE-QUAL-W2 Output – Turn on to link CE-QUAL-W2 output.
- Manage files – Turn on and click Edit parameters... to bring up the Save GSSHA Project File dialog.
GSSHA | |
|---|---|
| XMS Wiki Links | Calibration (Automated • Manual • Output) • Channel Routing • Contaminants • Digital Dams • Embankment Arcs • Feature Objects (Arcs • Nodes • Polygons) • File Types • Groundwater • Groups • Hydraulic Structures • Job Control • Join SSURGO Data • Mapping Tables • Maps • Menu • Model Linkage • Multiple Simulations • Nutrients • Observations • Output Control • Overland Soil Erosion • Pipe and Node Parameters • Precipitation • Radar Rainfall • Save GSSHA Project File • Smooth GSSHA Streams • Snowmelt • Solution (Analysis • Data) |
| Related Tools | MWBM Wizard • Using Soil Type Data with GSSHA |
| GSSHA Wiki External Links | GSSHA Wiki: Overview • Primer • User's Manual • Tutorials |
WMS – Watershed Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | Terrain Data • Drainage • Map • Hydrologic Modeling • River • GIS • 2D Grid • 2D Scatter |  |
| Models: | CE-QUAL-W2 • GSSHA • HEC-1 • HEC-HMS • HEC-RAS • HSPF • MODRAT • NSS • OC Hydrograph • OC Rational • Rational • River Tools • Storm Drain • SMPDBK • SWMM • TR-20 • TR-55 | |
| Toolbars: | Modules • Macros • Units • Digitize • Static Tools • Dynamic Tools • Drawing • Get Data Tools | |
| Aquaveo | ||